Question
Time left
Score
0
What is the answer to this questions?
A
Choice 1
B
Choice 2
C
Choice 3
D
Choice 4
1
Azure virtual networks
- Azure virtual networks enable Azure resources, such as virtual machines, web apps, and databases, to communicate with: each other, users on the internet, and on-premises client computers. You can think of an Azure network as a set of resources that links other Azure resources.
- Azure virtual networks provide key networking capabilities: (Isolation and segmentation
Internet communications,
Communicate between Azure resources,
Communicate with on-premises resources,
Route network traffic,
Filter network traffic,
Connect virtual networks)
2
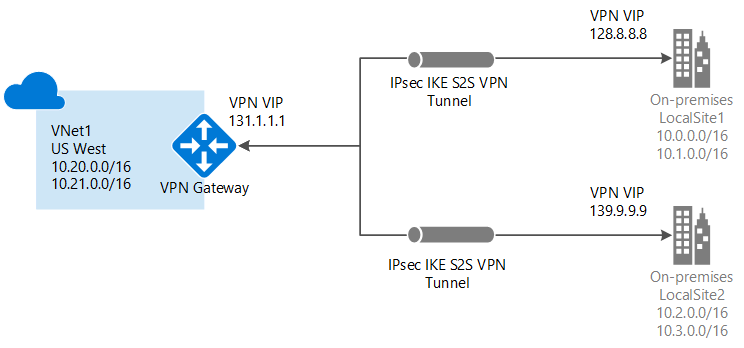
What is a VPN gateway?
- An Azure virtual network gateway provides an endpoint for incoming connections from on-premises locations to Azure over the Internet. A VPN gateway is a specific type of virtual network gateway that can be an endpoint for encrypted connections. It can also send encrypted traffic between Azure virtual networks over Microsoft's dedicated network that links Azure datacenters in different regions. This configuration enables you to link virtual machines and services in different regions securely.
- Each virtual network can have only one VPN gateway. All connections to that VPN gateway share the available network bandwidth.
- Within each virtual network gateway there are two or more virtual machines (VMs). These VMs have been deployed to a special subnet that you specify, called the gateway subnet. They contain routing tables for connections to other networks, along with specific gateway services. These VMs and the gateway subnet are similar to a hardened network device. You don't need to configure these VMs directly, and should not deploy any additional resources into the gateway subnet.
-
3
Plan a VPN gateway
When you're planning a VPN gateway, there are three architectures to consider:
- Point to site over the internet
- Site to site over the internet
- Site to site over a dedicated network, such as Azure ExpressRoute
4
Set up a VPN gateway
The steps you need to take will depend on the type of VPN gateway that you are installing. For example, to create a point-to-site VPN gateway by using the Azure portal, you would perform the following steps:
- Create a virtual network.
- Add a gateway subnet.
- Specify a DNS server (optional).
- Create a virtual network gateway.
- Generate certificates.
- Add the client address pool.
- Configure the tunnel type.
- Configure the authentication type.
- Upload the root certificate public certificate data.
- Install an exported client certificate.
- Generate and install the VPN client configuration package.
- Connect to Azure.
5
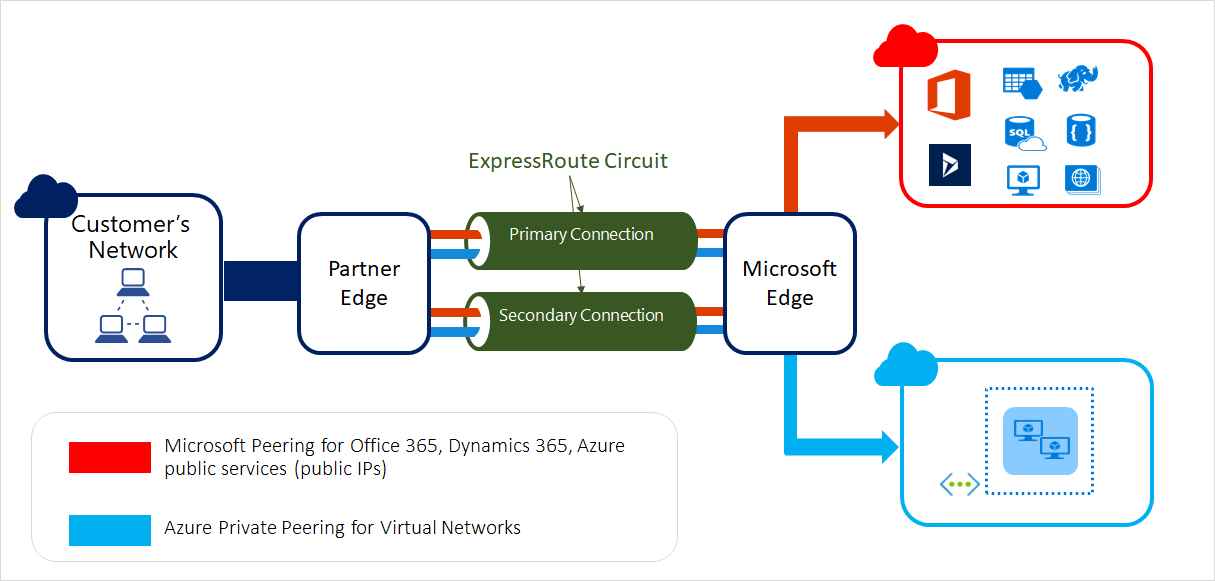
Azure ExpressRoute
Microsoft Azure ExpressRoute enables organizations to extend their on-premises networks into the Microsoft Cloud over a private connection implemented by a connectivity provider. This arrangement means that the connectivity to the Azure datacenters doesn't go over the internet but across a dedicated link. ExpressRoute also facilitates efficient connections with other Microsoft cloud-based services, such as Microsoft 365 and Dynamics 365.
Advantages that ExpressRoute provides include:
- Faster speeds, from 50 Mbps to 10 Gbps, with dynamic bandwidth scaling
- Lower latency
- Greater reliability through built-in peering
- Highly secure
- Connectivity to all supported Azure services
- Global connectivity to all regions (requires premium add-on)
- Dynamic routing over Border Gateway Protocol
- Service-level agreements (SLAs) for connection uptime
- Quality of Service (QoS) for Skype for Business
6
For a point-to-site Azure VPN gateway, what are the key parameters that you must specify when you create it?
- Gateway type is Vpn, vpn type is RouteBased, and you need to specify a gateway sku.
- Use the PowerShell cmdlet 'New-AzVirtualNetworkGateway' where you use parameters '-GatewayType Vpn' and '-VpnType RouteBased'. Also set the '-GatewaySku' to the SKU that meets your organization's network requirements.
7
Which peering configuration would you use for your Express route circuit where you need to allow direct connections to Azure compute resources?
- Azure private peering lets you directly connect to virtual machines and cloud services on their private IP addresses.
8
Which protocol provides dynamic routing for Azure ExpressRoute?
- Border Gateway Protocol is an industry-standard dynamic routing protocol that can exchange routes between your on-premises network, your instances in Azure, and Microsoft public addresses.
9
When assigning private IPv4 addresses in a subnet with the address range 10.2.0.0/16, which of the following addresses are available for assignment dynamically? [
10.2.0.2
10.2.255.255
10.2.255.254
-Any address in the range 10.2.0.4 through 10.2.255.254 is available for assignment.
10
The infrastructure team has two NSG security rules for inbound traffic to the backend web servers. There is an allow rule with a priority of 200. And, there is a deny rule with a priority of 150. Which rule takes precedence?
- The deny rule takes precedence
- The deny rule takes precedence because it's processed first. The rule with priority 150 is processed before the rule with priority 200.
11
Which of the following resources could have a public IP address? [1- VM, 2- Azure Data Lake, 3- Azure Key Vault]
- Public IP addresses can be assigned to virtual machines.
12
Suppose a company wants to allow access to an Azure SQL Database instance. Which of the following network rule types should they use to configure Azure firewall? [1- Application , 2-
Network , 3- Tag ]
- An application rule can be used to filter traffic based on an FQDN such as server1.database.windows.net.
13
What type of DNS record should be created to map one or more IP addresses against a single domain?
- The A or AAAA record maps an IP address to a domain. Multiple IP addresses are known as a record set.
14
True or False: Azure Private DNS lets organizations manage and resolve domain names in a virtual network without adding a custom DNS solution.
- True: Azure Private DNS manages and resolves domain names in a virtual network without adding a custom DNS solution.
15
Virtual network peering is successfully established when the peering status for both virtual network peerings shows which status?
- The peering is not successfully established until the peering status for both virtual network peerings is Connected.
16
Which service allows peered virtual networks to share the gateway and get access to resources?
- Gateway transit allows peered virtual networks to share the gateway and get access to resources.
17
What best describes virtual network peering?
-
Traffic between the virtual networks is kept on the Microsoft backbone network. The Azure backbone handles traffic between virtual networks.
18
The company's VPN gateway must work with ExpressRoute. Which VPN type should be used?
- Route-based: Typical route-based gateway scenarios include point-to-site, inter-virtual network, or multiple site-to-site connections. Route-based is also selected to coexist with an ExpressRoute gateway or when the IKEv2 protocol is used.
19
What is the Azure ExpressRoute service?
- Azure ExpressRoute is a service that provides a direct connection from the on-premises datacenter to the Microsoft cloud.
20
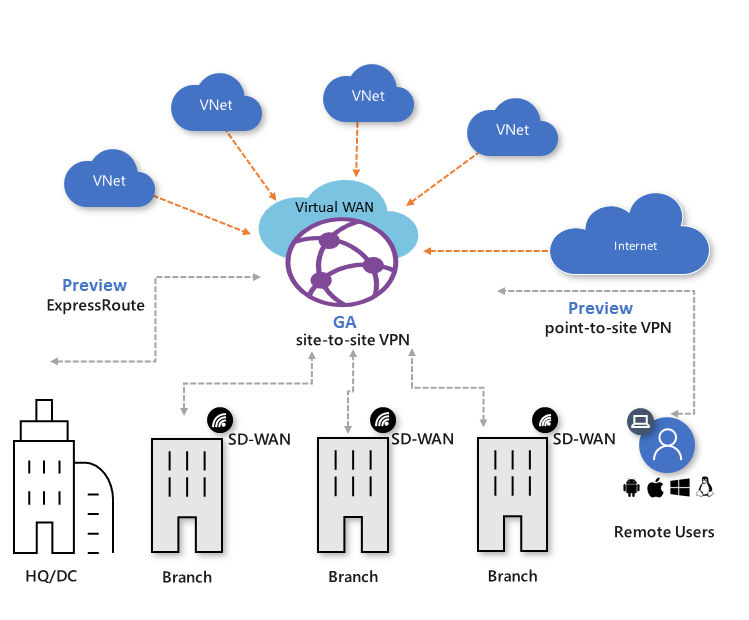
What Microsoft service helps to simplify a complex hub-and-spoke virtual network WAN deployment?
- Azure Virtual WAN with Virtual WAN hubs simplifies a complex virtual network WAN.
21
When should Azure ExpressRoute be used instead of Azure site-to-site connectivity?
- ExpressRoute is best for handling enterprise-class and mission-critical workloads.
22
A company provides customers a virtual network in the cloud. There are dozens of Linux virtual machines in another virtual network. Which Azure load balancer should be used to direct traffic between the virtual networks?
- An internal load balancer directs traffic only to resources that are inside a virtual network or that use a VPN to access Azure infrastructure.
23
What is the default distribution type for traffic through a load balancer?
- The load balancer uses a five-tuple (source IP, source port, destination IP, destination port, and protocol type) hash to map traffic to available servers.
24
Which configuration is required for an internal load balancer?
- Virtual machines should be in the same virtual network
- The virtual machines that use a load balancer to distribute a load to must be in the same virtual network.
25
Which criteria does Application Gateway use to route requests to a web server?
- The hostname, port, and path in the URL of the request.
- An Application Gateway uses the hostname, port and URL path.
26
Which load balancing strategy does the Application Gateway implement?
- The Application Gateway distributes requests using round-robin.
27
When installing Application Gateway, how to ensure incoming requests are checked for common security threats like cross-site scripting and crawlers.
- Install the Web Application Firewall
- The Web Application Firewall is an optional component that handles incoming requests before they reach a listener. The Web Application Firewall checks each request for many common threats, based on the Open Web Application Security Project.
28
What is the default distribution type for traffic through a load balancer?
- Five-tuple hash is the default.
29
What is the main advantage of an availability set?
- Availabilty sets allow virtual machines to remain available when a physical server fails.
29
Which configuration is required to configure an internal load balancer?
- The virtual machines that you use a load balancer to distribute a load to must be in the same virtual network.
30
Why would you use a custom route in a virtual network?
- To control the flow of traffic within your Azure virtual network
- Custom routes are used to override the default Azure routing so that you can route traffic through a network virtual appliance (NVA).
31
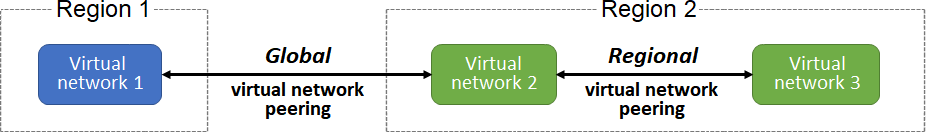
Why might you use virtual network peering?
- To connect virtual networks together in the same region or across regions
- Virtual network peering is used to connect multiple virtual networks together. Once peered, the networks become one network, and resources across virtual networks can communicate with one another.
32
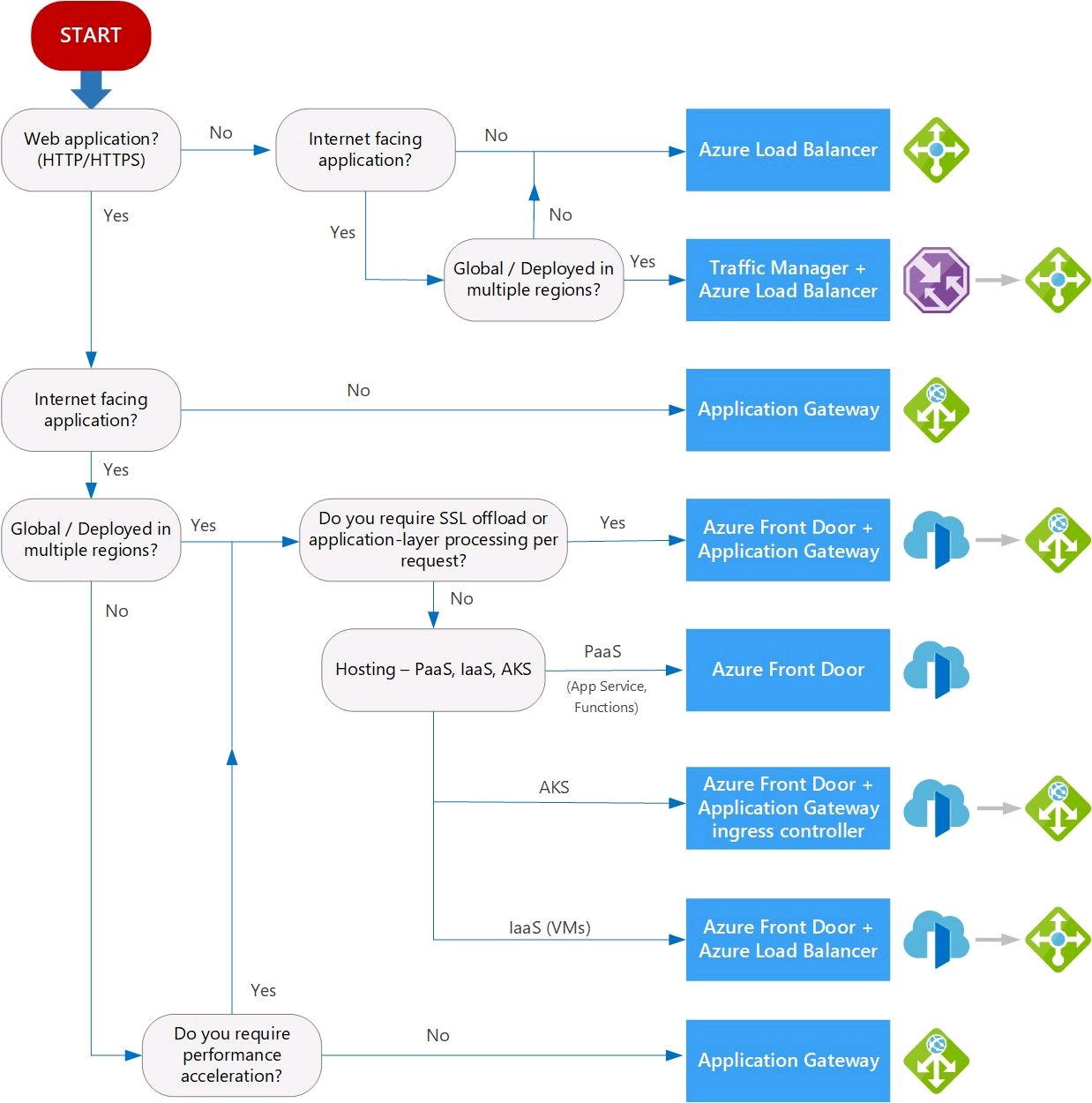
Azure Load Balancing Cheat Sheets
- Azure load balancing services can be categorized along two dimensions: Global 🌎 versus Regional 📍, and HTTP(S) versus non-HTTP(S).
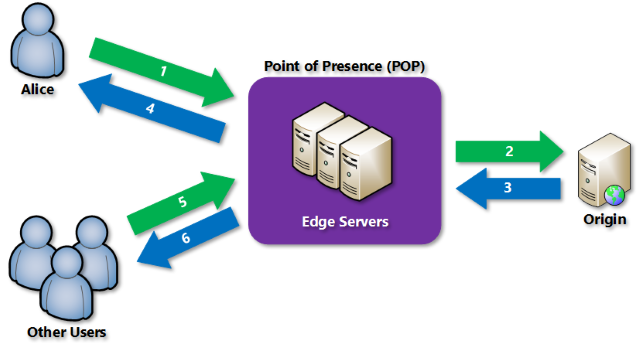
- FrontDoor is an application delivery network that provides global load balancing and site acceleration service for web applications. It offers Layer 7 capabilities for your application like SSL offload, path-based routing, fast failover, caching, etc. to improve performance and high-availability of your applications.
- TrafficManager is a DNS-based traffic load balancer that enables you to distribute traffic optimally to services across global Azure regions, while providing high availability and responsiveness. Because Traffic Manager is a DNS-based load-balancing service, it load balances only at the domain level. For that reason, it can't fail over as quickly as Front Door, because of common challenges around DNS caching and systems not honoring DNS TTLs.
- ApplicationGateway provides application delivery controller (ADC) as a service, offering various Layer 7 load-balancing capabilities. Use it to optimize web farm productivity by offloading CPU-intensive SSL termination to the gateway.
- AzureLoadBalancer is a high-performance, ultra low-latency Layer 4 load-balancing service (inbound and outbound) for all UDP and TCP protocols. It is built to handle millions of requests per second while ensuring your solution is highly available. Azure Load Balancer is zone-redundant, ensuring high availability across Availability Zones.
- If your application consists of multiple workloads, evaluate each workload separately. A complete solution may incorporate two or more load-balancing solutions.
-
Azure Administrator AZ104 Certification Exam Preparation
Azure Networking Services Illustration Slideshow
Below are the skills measured in this category:
Configure and manage virtual networking (25–30%)
1
Implement and manage virtual networking
- create and configure virtual networks, including peering
- configure private and public IP addresses
- configure user-defined network routes
- implement subnets
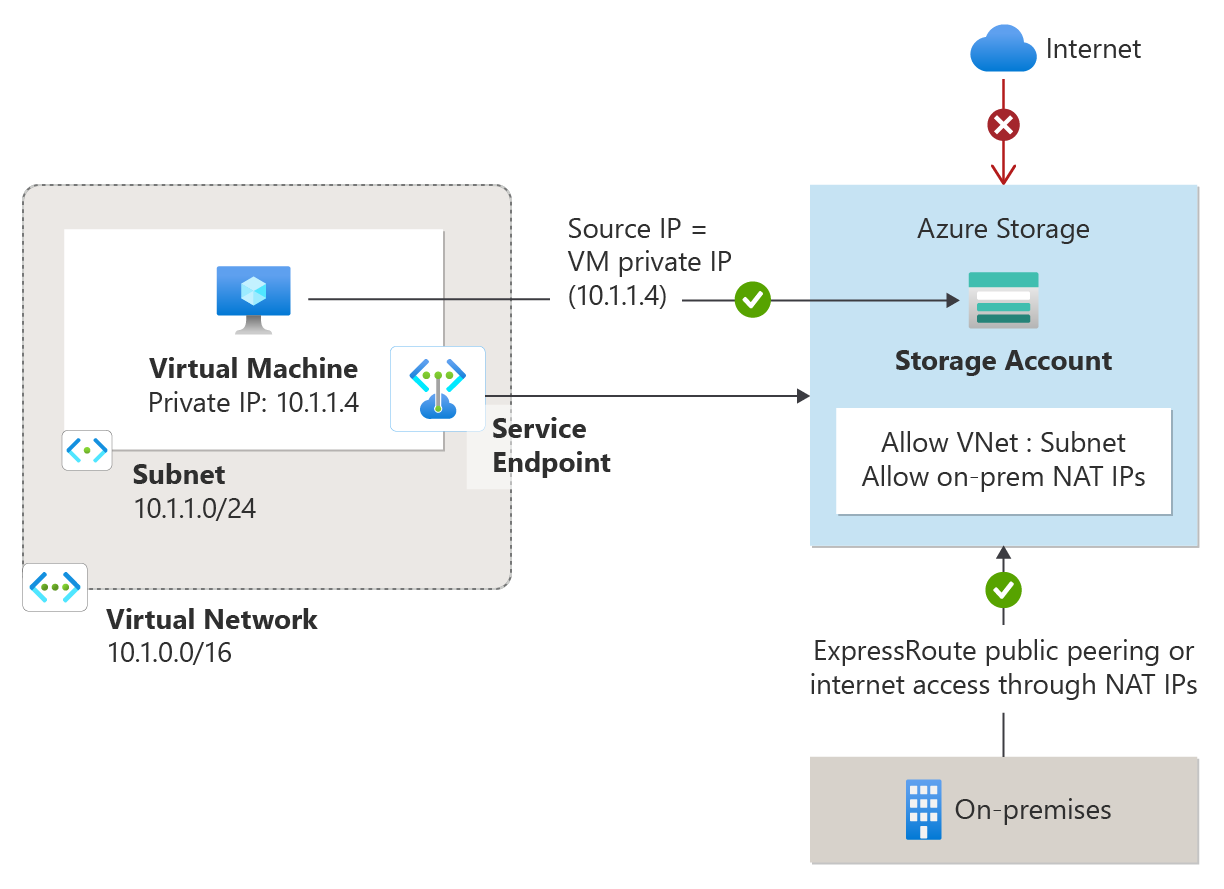
- configure endpoints on subnets
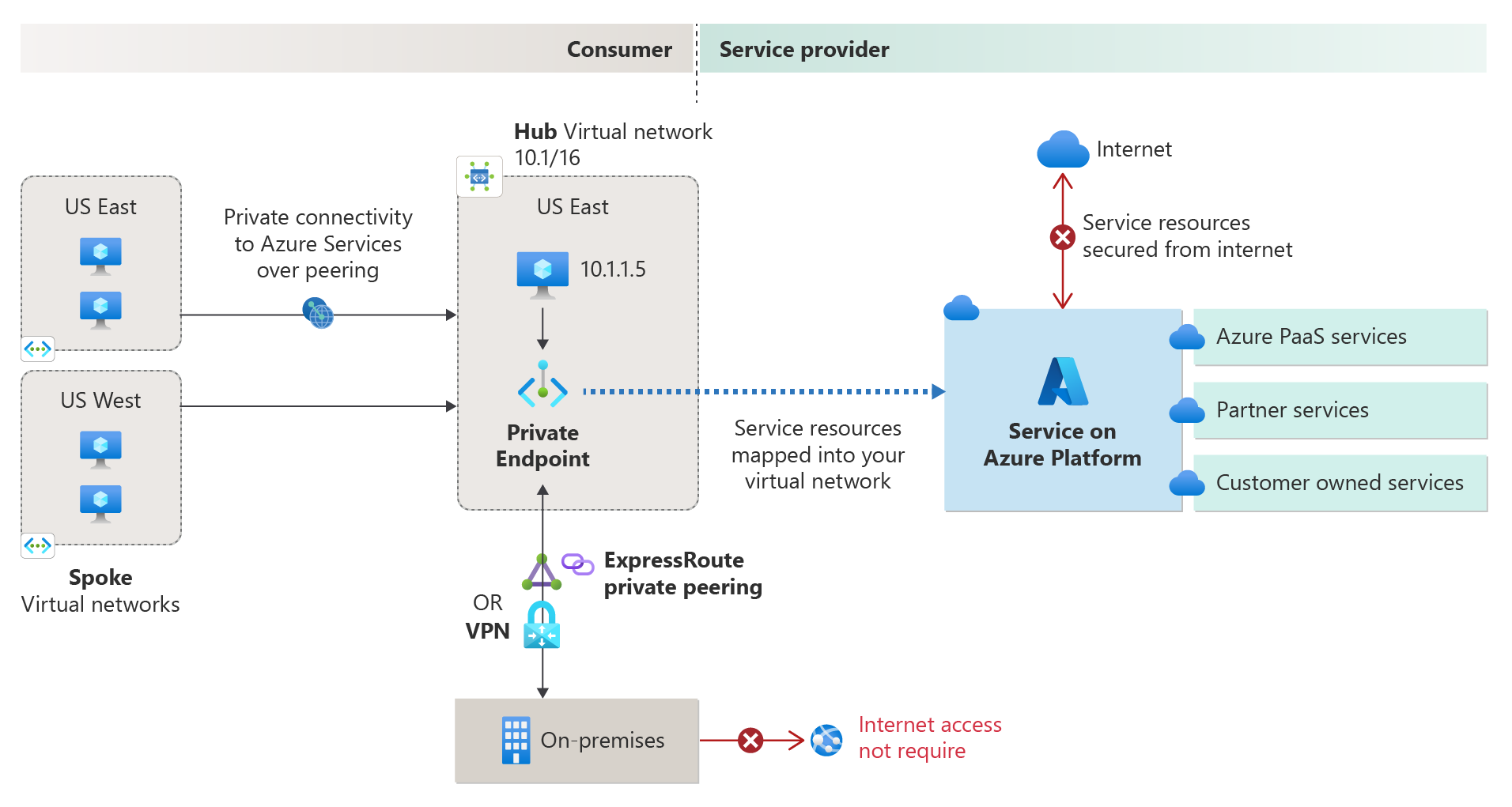
- configure private endpoints
- configure Azure DNS, including custom DNS settings and private or public DNS zones
2
Secure access to virtual networks
- create security rules
- associate a network security group (NSG) to a subnet or network interface
- evaluate effective security rules
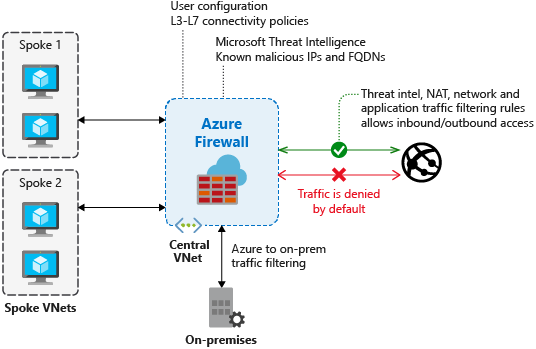
- implement Azure Firewall
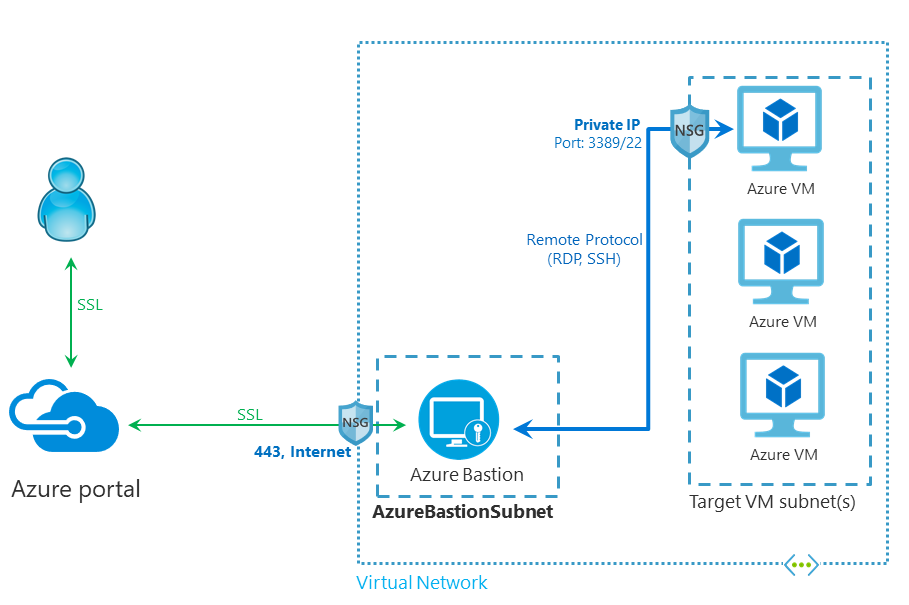
- implement Azure Bastion
3
Configure load balancing
- configure Azure Application Gateway
- configure an internal or public load balancer
- troubleshoot load balancing
4
Monitor and troubleshoot virtual networking
- monitor on-premises connectivity
- configure and use Network Performance Monitor
- use Azure Network Watcher
- troubleshoot external networking
- troubleshoot virtual network connectivity
5
Integrate an on-premises network with an Azure virtual network
- create and configure Azure VPN Gateway
- create and configure Azure ExpressRoute
- configure Azure Virtual WAN