0
What is cloud computing?
It's the delivery of computing services over the internet, which is otherwise known as the cloud. These services include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence. Cloud computing offers faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
1
What are some cloud computing advantages?
Reliability: Depending on the service-level agreement that you choose, your cloud-based applications can provide a continuous user experience with no apparent downtime even when things go wrong.
Scalability: Applications in the cloud can be scaled in two ways, while taking advantage of autoscaling:
- Vertically: Computing capacity can be increased by adding RAM or CPUs to a virtual machine.
- Horizontally: Computing capacity can be increased by adding instances of a resource, such as adding more virtual machines to your configuration.
Elasticity: Cloud-based applications can be configured to always have the resources they need.
Agility: Cloud-based resources can be deployed and configured quickly as your application requirements change.
Geo-distribution: Applications and data can be deployed to regional datacenters around the globe, so your customers always have the best performance in their region.
Disaster recovery: By taking advantage of cloud-based backup services, data replication, and geo-distribution, you can deploy your applications with the confidence that comes from knowing that your data is safe in the event that disaster should occur.
2
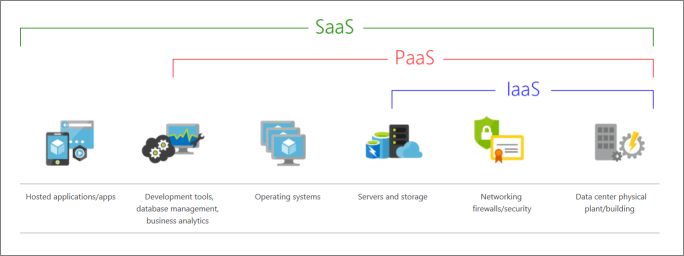
What are cloud service models?
IAAS:
This cloud service model is the closest to managing physical servers. A cloud provider keeps the hardware up to date, but operating system maintenance and network configuration is left to the cloud tenant. For example, Azure virtual machines are fully operational virtual compute devices running in Microsoft's datacenters. An advantage of this cloud service model is rapid deployment of new compute devices. Setting up a new virtual machine is considerably faster than procuring, installing, and configuring a physical server.
SAAS:
In this cloud service model, the cloud provider manages all aspects of the application environment, such as virtual machines, networking resources, data storage, and applications. The cloud tenant only needs to provide their data to the application managed by the cloud provider. For example, Office 365 provides a fully working version of Office that runs in the cloud. All that you need to do is create your content, and Office 365 takes care of everything else.
PAAS
This cloud service model is a managed hosting environment. The cloud provider manages the virtual machines and networking resources, and the cloud tenant deploys their applications into the managed hosting environment. For example, Azure App Services provides a managed hosting environment where developers can upload their web applications without having to deal with the physical hardware and software requirements.
DAAS
DAAS is a form of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), hosted in the cloud. With VDI, an organization deploys virtual desktops from its own on-premises data centers. In-house IT teams are responsible for deploying the virtual desktops as well as purchasing, managing, and upgrading the infrastructure.
3
What is serverless computing?
Overlapping with PaaS, serverless computing enables developers to build applications faster by eliminating the need for them to manage infrastructure. With serverless applications, the cloud service provider automatically provisions, scales, and manages the infrastructure required to run the code. Serverless architectures are highly scalable and event-driven. They use resources only when a specific function or trigger occurs.
4
What are public, private, and hybrid clouds?
Public cloud Services are offered over the public internet and available to anyone who wants to purchase them. Cloud resources like servers and storage are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider and delivered over the internet.
Private cloud Computing resources are used exclusively by users from one business or organization. A private cloud can be physically located at your organization's on-site datacenter. It also can be hosted by a third-party service provider.
Hybrid cloud This computing environment combines a public cloud and a private cloud by allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
5
What can I do with Azure?
Azure provides more than 100 services that enable you to do everything from running your existing applications on virtual machines to exploring new software paradigms, such as intelligent bots and mixed reality.
Many teams start exploring the cloud by moving their existing applications to virtual machines that run in Azure. Migrating your existing apps to virtual machines is a good start, but the cloud is much more than a different place to run your virtual machines.
For example, Azure provides AI and machine-learning services that can naturally communicate with your users through vision, hearing, and speech. It also provides storage solutions that dynamically grow to accommodate massive amounts of data. Azure services enable solutions that aren't feasible without the power of the cloud.
6
What is a benefit of a hybrid cloud approach?
A hybrid cloud solution can offer the best of public cloud and on-premises services for many companies. A hybrid solution enables businesses to use a mix of on-premises infrastructure whilst scaling certain resources in the cloud.
Reference:Azure hybrid cloud approach
7
What is high availability in cloud computing?
High availability is one of the core benefits of using cloud computing. It ensures that backup resources are ready to take over any workload
Reference:Azure High Availability
8
Why is cloud agility important for businesses?
Cloud agility is tied to the rapid provisioning of computer resources. Cloud environments can usually provide new compute instances or storage in minutes, a far cry from the very common weeks (or months, in some organizations) the same provisioning process can take in typical IT shops.
Reference:Cloud Agility
9
What is the difference between OPEX and CAPEX?
OPEX is an ongoing cost for running a business. CAPEX is the cost of acquiring assets..
Knowing the difference between OPEX and CAPEX is critical to get the best value out of Azure for your company. Capital Expenditures (CAPEX) are generally not recurring and result in the acquisition of assets, such as server hardware. Operating Expenditures (OPEX) are the ongoing costs of running a business, such as paying for cloud services on a recurring basis. By moving costs to OPEX, businesses can plan for ongoing costs rather than large investments.
Reference:OPEX vs CAPEX
10
Which cloud ability does elasticity describe?
Elasticity is a core benefit of cloud computing and lets even small businesses take advantage of the cloud.
Reference:Azure elasticity
0
Azure Cosmos DB
Azure Cosmos DB is a globally distributed, multi-model database service. You can elastically and independently scale throughput and storage across any number of Azure regions worldwide. You can take advantage of fast, single-digit-millisecond data access by using any one of several popular APIs. Azure Cosmos DB provides comprehensive service level agreements for throughput, latency, availability, and consistency guarantees.
2
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database is a relational database based on the latest stable version of the Microsoft SQL Server database engine. SQL Database is a high-performance, reliable, fully managed, and secure database. You can use it to build data-driven applications and websites in the programming language of your choice, without needing to manage infrastructure.
3
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure SQL Managed Instance is a scalable cloud data service that provides the broadest SQL Server database engine compatibility with all the benefits of a fully managed platform as a service. Depending on your scenario, Azure SQL Managed Instance might offer more options for your database needs.
4
Azure compute
Azure compute is an on-demand computing service for running cloud-based applications. It provides computing resources such as disks, processors, memory, networking, and operating systems. The resources are available on-demand and can typically be made available in minutes or even seconds. You pay only for the resources you use, and only for as long as you're using them.
Azure supports a wide range of computing solutions for development and testing, running applications, and extending your datacenter. The service supports Linux, Windows Server, SQL Server, Oracle, IBM, and SAP. Azure also has many services that can run virtual machines (VMs). Each service provides different options depending on your requirements. Some of the most prominent services are:
- Azure Virtual Machines
- Azure Container Instances
- Azure App Service
- Azure Functions (or serverless computing)
5
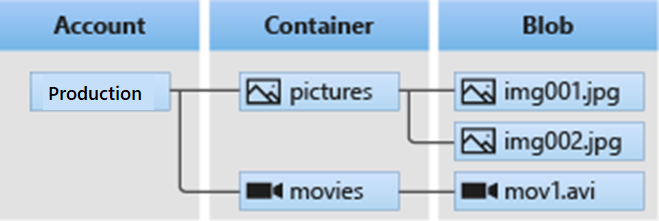
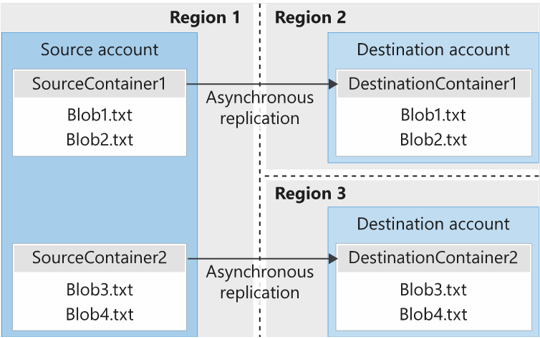
Azure Storage
Azure Storage is a service that you can use to store files, messages, tables, and other types of information. Clients such as websites, mobile apps, desktop applications, and many other types of custom solutions can read data from and write data to Azure Storage. Azure Storage is also used by infrastructure as a service virtual machines, and platform as a service cloud services.
Here are different types of Azure storage:
Azure Blob Storage: object storage solution for the cloud. It can store massive amounts of data, such as text or binary data.
Azure Disk Storage: provides disks for Azure virtual machines.
Azure Files Storage: fully managed file shares in the cloud that are accessible via the industry standard Server Message Block and Network File System (preview) protocols.
Azure Blob Access tiers: Hot access tier, Cool access tier, Archive access tier
6
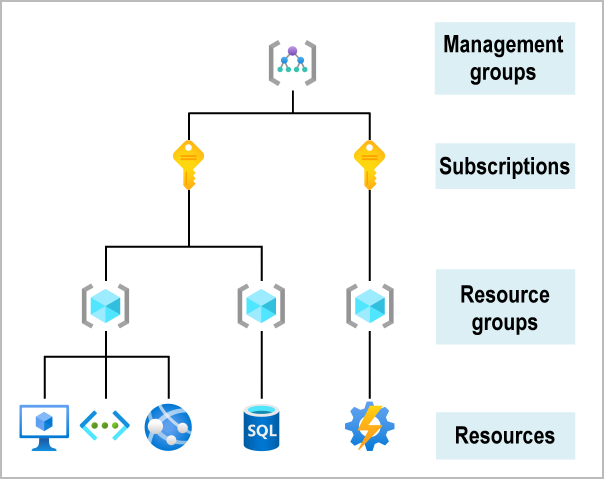
What is the purpose of the Resource Manager in Azure?
The Azure Resource Manager is the common architectural layer which all commands must go through to interact with Azure resources. The Resource Manager manages all resources on Azure, and is the only tool that creates resources on Azure.
Reference:Azure Resource Manager
7
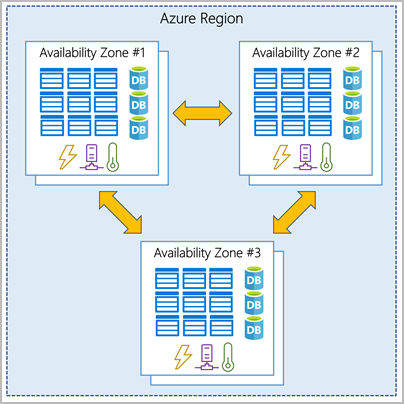
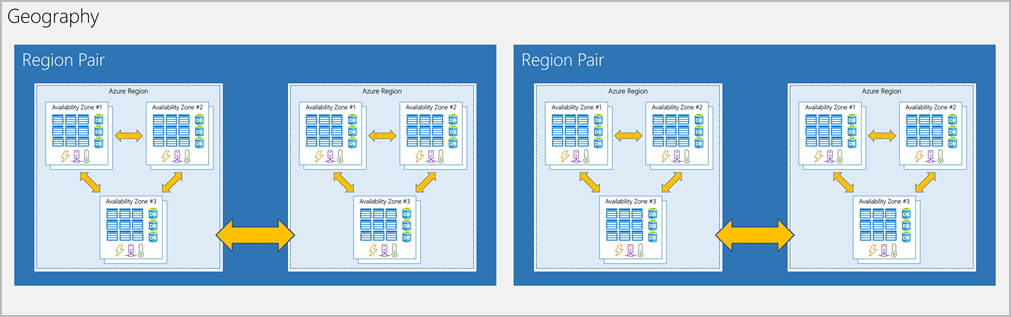
What is an availability zone?
AZs are individual physical locations within a region. Each zone is made up of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking.
Reference:Azure availability zones
8
What is a scale set?
Azure virtual machine scale sets let you create and manage a group of load balanced VMs. The number of VM instances can automatically increase or decrease in response to demand or a defined schedule. Scale sets provide high availability to your applications, and allow you to centrally manage, configure, and update a large number of VMs. With virtual machine scale sets, you can build large-scale services for areas such as compute, big data, and container workloads
Reference:
9
What is a fully managed platform on Azure?
A fully managed platform means the provider manages the infrastructure layer, such as VMs, disks, networks and more. You only have to focus on the core functionality of your application. Fully managed services on Azure are available on all subscription types and comes at no extra cost.
Reference:Managed platform on Azure
10
What is an Azure Function?
Azure Functions are single-task services that can take an input, process it, and then die. It is the first serverless product on Azure. It is a stand-alone product which doesn't rely on other Azure services, although Functions can certainly integrate with them. Functions are available on all subscriptions and are very inexpensive to use.
Reference:Azure Functions
0
TCO Calculator
The TCO Calculator helps you estimate the cost savings of operating your solution on Azure over time, instead of in your on-premises datacenter.
With the TCO Calculator, you enter the details of your on-premises workloads. Then you review the suggested industry average cost (which you can adjust) for related operational costs. These costs include electricity, network maintenance, and IT labor. You're then presented with a side-by-side report. Using the report, you can compare those costs with the same workloads running on Azure.
1
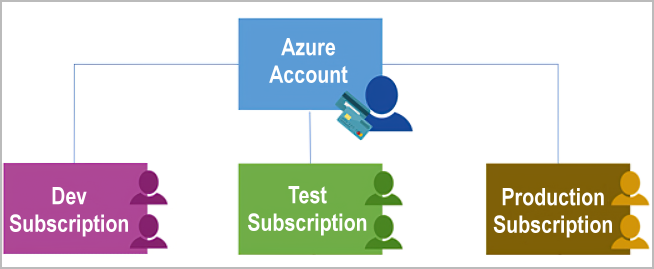
What types of Azure subscriptions can I use?
- Free trial
A free trial subscription provides you with 12 months of popular free services, a credit to explore any Azure service for 30 days, and more than 25 services that are always free. Your Azure services are disabled when the trial ends or when your credit expires for paid products, unless you upgrade to a paid subscription.
- Pay As You Go
A pay-as-you-go subscription enables you to pay for what you use by attaching a credit or debit card to your account. Organizations can apply for volume discounts and prepaid invoicing.
-Member offers
our existing membership to certain Microsoft products and services might provide you with credits for your Azure account and reduced rates on Azure services. For example, member offers are available to Visual Studio subscribers, Microsoft Partner Network members, Microsoft for Startups members, and Microsoft Imagine members.
3
What factors affect cost?
The way you use resources, your subscription type, and pricing from third-party vendors are common factors.
- Resource type
- Usage meters
- Resource usage
- Azure subscription types
- Azure Marketplace
4
Does location or network traffic affect cost?
When you provision a resource in Azure, you need to define the location (known as the Azure region) of where it will be deployed. Let's see why this decision can have cost consequences.
- Location
Different regions can have different associated prices. Because geographic regions can impact where your network traffic flows, network traffic is a cost influence to consider as well.
- Zones for billing of network traffic
Billing zones are a factor in determining the cost of some Azure services.Bandwidth refers to data moving in and out of Azure datacenters. Some inbound data transfers (data going into Azure datacenters) are free. For outbound data transfers (data leaving Azure datacenters), data transfer pricing is based on zones.
5
How can I estimate the total cost?
The Pricing calculator displays Azure products in categories. You add these categories to your estimate and configure according to your specific requirements. You then receive a consolidated estimated price, with a detailed breakdown of the costs associated with each resource you added to your solution. You can export or share that estimate or save it for later. You can load a saved estimate and modify it to match updated requirements.
You also can access pricing details, product details, and documentation for each product from within the Pricing calculator.
6
How do you sign up for a service level agreement with Azure?
Service Level Agreements are implicit for all Azure paid services. You get an SLA included with every subscription level and support level. In general, there are no SLAs associated with free products on Azure.
Reference:Service level agreement with Azure
7
What kind of questions and answers can you find in the Azure Knowledge Center?
The Knowledge Center provides answers to a range of the most common questions asked. The focus is in particular on foundational answers, or answers to popular questions that are seen again and again. Users can't submit questions nor answers, and there are few to no expert level articles.
Reference:Knowledge Center
8
What is the response time for Severity B on the Professional Direct Support Plan?
The Professional support agreement is not quite as fast as one hour response. It is 2 hours.
Reference:Response Time for Severity B on the Professional Direct Support Plan
9
Which are valid support channels for Azure?
The Azure documentation, technical forums and official Azure social media accounts are all good ways to interact with experts and Azure professionals. There is no regional standard phone support. Pressing all the buttons may be fun, but you might also pay for that new NS48 v3 virtual machine at $6.8 per hour.
Reference:Azure Support Channels
10
Where can you open a new Azure support request
A support request can only be opened via the Azure Portal.
Reference:Azure Portal
0
Azure DDoS Protection
Protects Azure-hosted applications from distributed denial of service (DDOS) attacks.
1
Azure ExpressRoute
Connects to Azure over high-bandwidth dedicated secure connections.
2
Azure Firewall
Implements high-security, high-availability firewall with unlimited scalability.
3
Azure Key Vault
Azure Key Vault is a centralized cloud service for storing an application's secrets in a single, central location. It provides secure access to sensitive information by providing access control and logging capabilities.
Azure Key Vault can help you: Manage secrets, Manage encryption keys, Manage SSL/TLS certificates, Store secrets backed by hardware security modules (HSMs) etc..
The benefits of using Key Vault include:
- Centralized application secrets
- Securely stored secrets and keys
- Access monitoring and access control
- Simplified administration of application secrets
- Integration with other Azure services
4
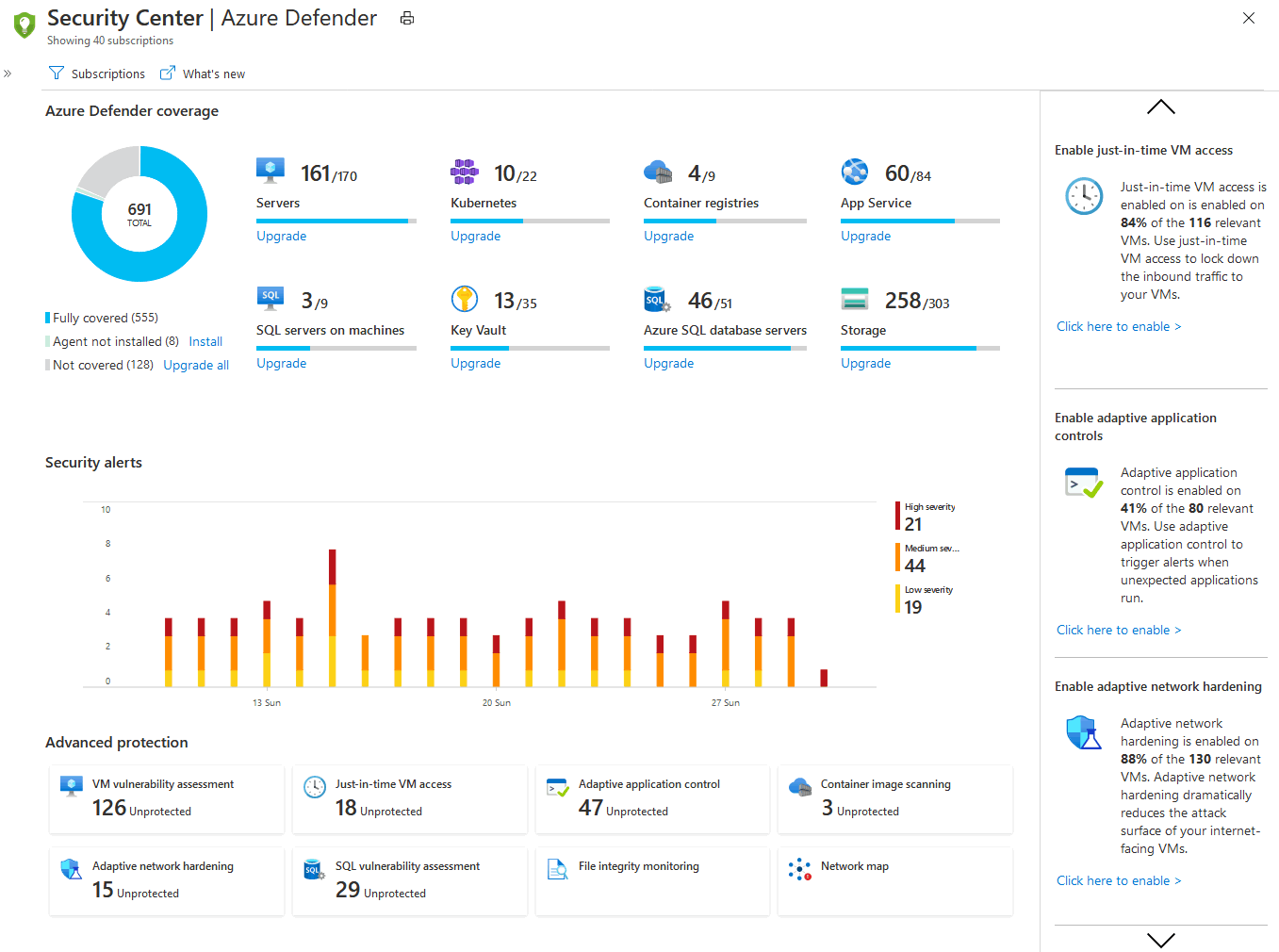
What's Azure Security Center?
Azure Security Center is a monitoring service that provides visibility of your security posture across all of your services, both on Azure and on-premises. The term security posture refers to cybersecurity policies and controls, as well as how well you can predict, prevent, and respond to security threats.
Security Center can:
- Monitor security settings across on-premises and cloud workloads.
- Automatically apply required security settings to new resources as they come online.
- Provide security recommendations that are based on your current configurations, resources, and networks.
- Continuously monitor your resources and perform automatic security assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities before those vulnerabilities can be exploited.
- Use machine learning to detect and block malware from being installed on your virtual machines (VMs) and other resources. You can also use adaptive application controls to define rules that list allowed applications to ensure that only applications you allow can run.
- Detect and analyze potential inbound attacks and investigate threats and any post-breach activity that might have occurred.
- Provide just-in-time access control for network ports. Doing so reduces your attack surface by ensuring that the network only allows traffic that you require at the time that you need it to.
5
What's Azure Security Score?
Secure score is a measurement of an organization's security posture.
Secure score is based on security controls, or groups of related security recommendations. Your score is based on the percentage of security controls that you satisfy. The more security controls you satisfy, the higher the score you receive. Your score improves when you remediate all of the recommendations for a single resource within a control.
Secure score helps you:
- Report on the current state of your organization's security posture.
- Improve your security posture by providing discoverability, visibility, guidance, and control.
- Compare with benchmarks and establish key performance indicators (KPIs).
6
What's Azure Sentinel?
Azure Sentinel is Microsoft's cloud-based SIEM system. It uses intelligent security analytics and threat analysis.
Azure Sentinel enables you to:
- Collect cloud data at scale
Collect data across all users, devices, applications, and infrastructure, both on-premises and from multiple clouds.
- Detect previously undetected threats
- Minimize false positives by using Microsoft's comprehensive analytics and threat intelligence.
- Investigate threats with artificial intelligence
Examine suspicious activities at scale, tapping into years of cybersecurity experience from Microsoft.
- Respond to incidents rapidly
Utilize built-in orchestration and automation of common tasks.
7
What is a definition of Authentication?
Authentication is the process of determining that you are you. This is most commonly done using a username and password, but could also be with a fingerprint or face recognition.
Reference:Azure Authentication
8
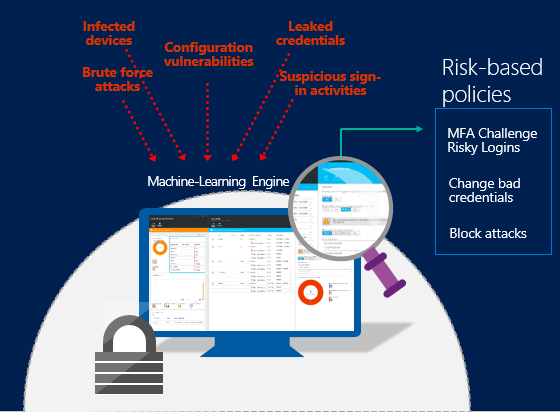
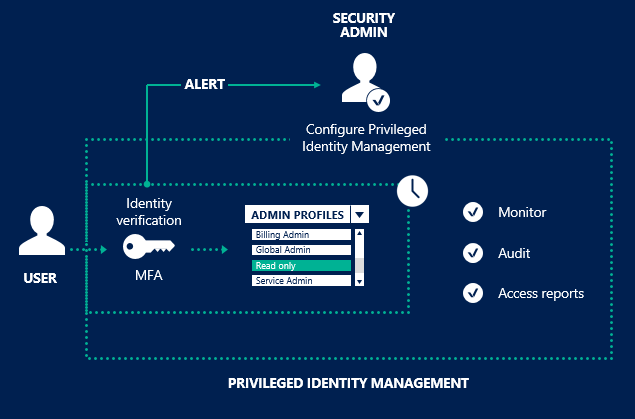
Which are factors used to verify a user with multi-factor authentication?
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) helps safeguard access to data and applications while maintaining simplicity for users. It provides additional security by requiring a second form of authentication and delivers strong authentication via a range of easy to use authentication methods, being something you know, have or are.
Reference:Azure MFA
9
Using Single Sign-On.
Single Sign-On lets users use a single username and password to access all apps registered with AAD.
Reference:Azure Single Sign On (SSO)
10
What does Advanced Threat Protection do?
Azure Advanced Threat Protection helps you detect and investigate security incidents across your Azure accounts both on-premises and in the cloud. It monitors users, devices and resources in terms of their behavior. If any behavior is out of the ordinary an alarm can be raised.
Reference:Azure Advanced Threat Protection
11
What is a distributed denial of service attack?
A distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack comes from a large number of sources with the sole aim of stopping your service. This is done through sending web traffic to your service until it can't handle it all and stops working. Azure has tools to protect against DDoS attacks, which sometimes aren't attacks at all, but just increased visitor interest in services or content.
Reference:Azure DDOS
12
What is a security policy in Security Center?
A security policy defines the desired configuration of your workloads and helps ensure you're complying with the security requirements of your company or regulators.
Reference:Azure Security Center
13
Which statements are true about Azure Key Vault?
Azure Key Vault is a secure place to store passwords and other secrets. Once stored, you can never retrieve the actual value, but you can share access to the value with other third party clients and other Azure services. You can also restrict or deny access easily and quickly, should it be necessary.
Reference:Azure Key Vault
14
What are features of role based access control?
Role-based access control (RBAC) helps you manage who has access to Azure resources, what they can do with those resources, and what areas they have access to. You have very detailed control of resource actions and you assign roles to users to let them take those actions. You can define as many roles as you wish in RBAC.
Reference:Azure Role-based access control (RBAC)
15
What are types of locks in Azure?
Locks can be put on resources to make sure there aren't any accidental or nefarious actions taken on them. The two types of locks are delete, which means you can't delete the resource, and "read only", which means you can't make any changes to the resources.
Reference:Azure locks types
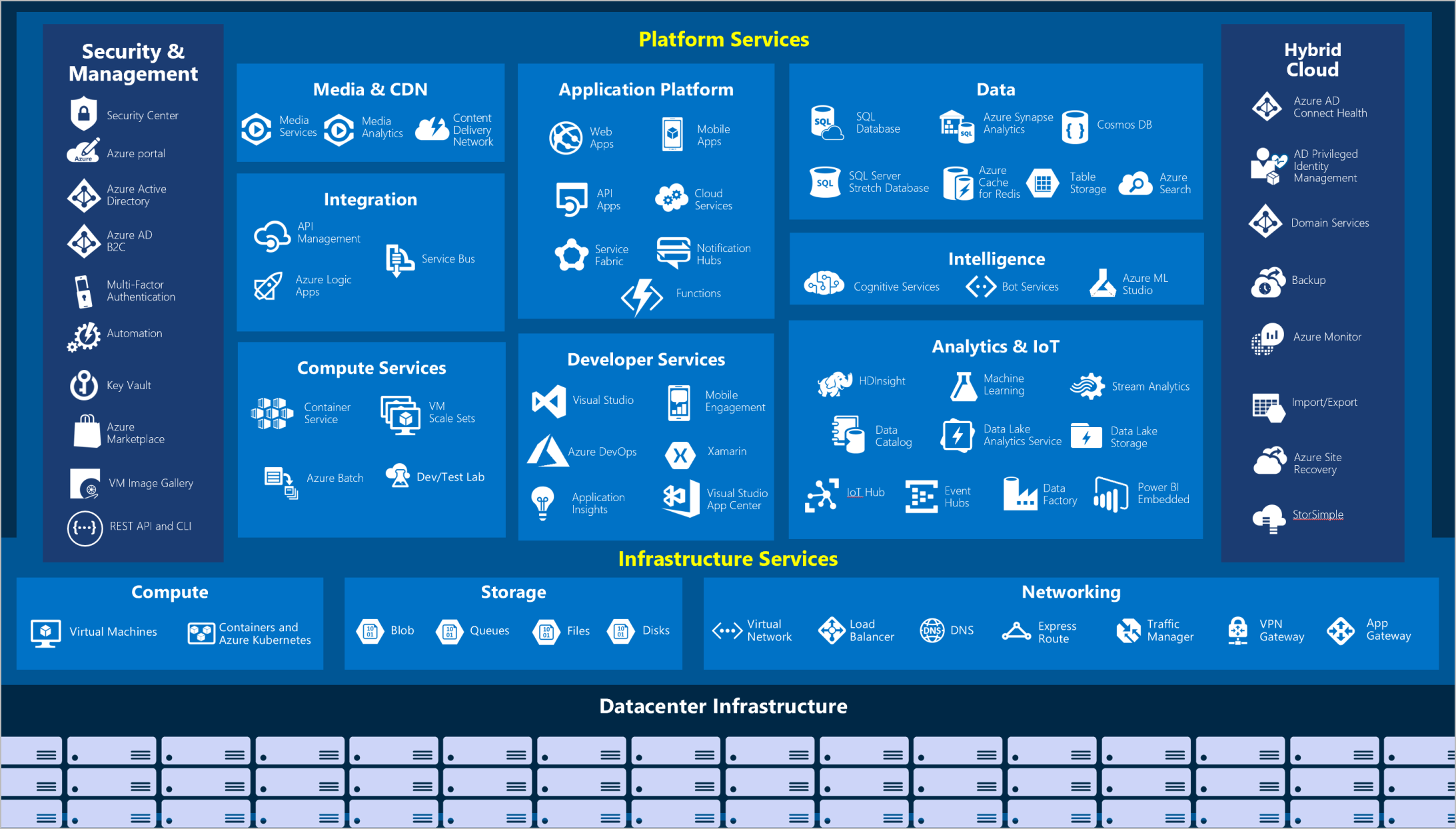
How does Azure work?


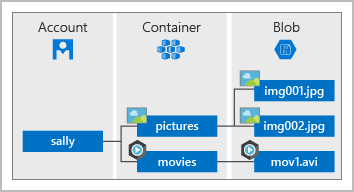

What are Azure Cloud Concepts?



How does Azure Security and Privacy work?
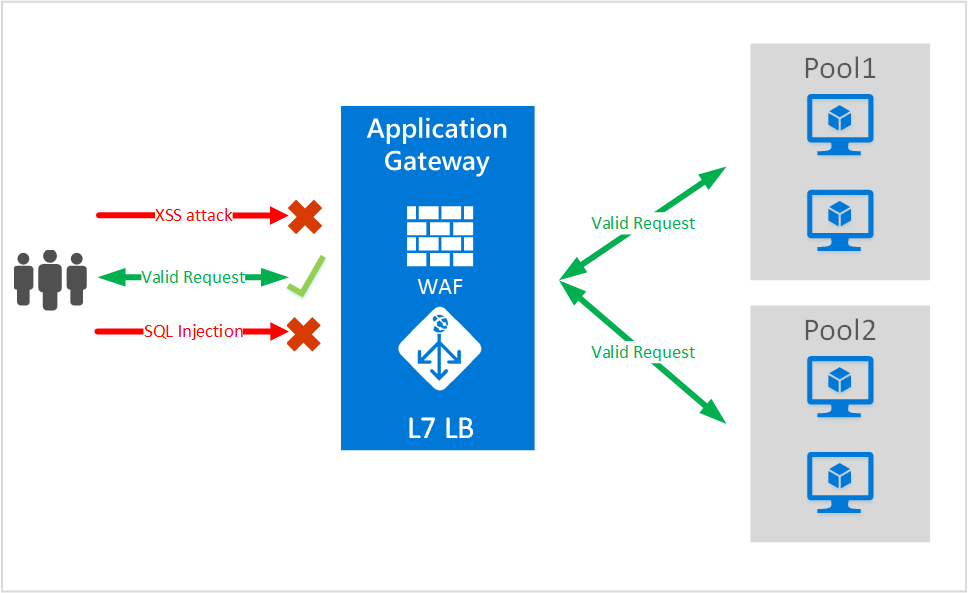
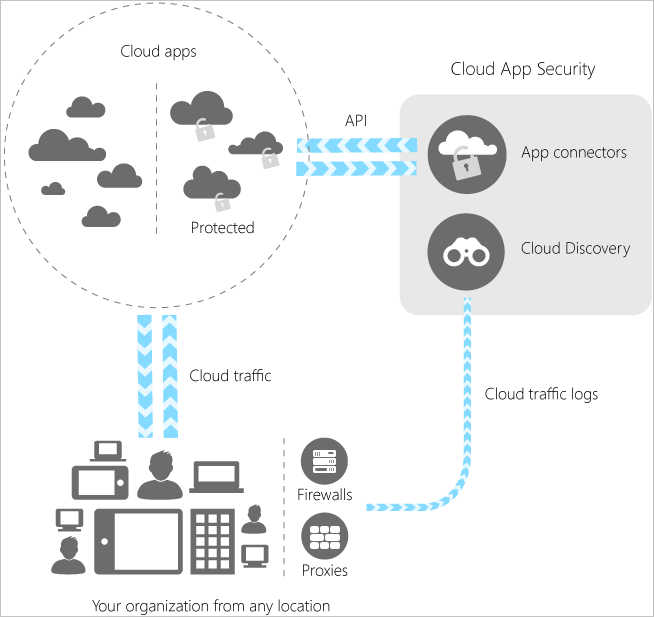
How does Azure Pricing and Support work?
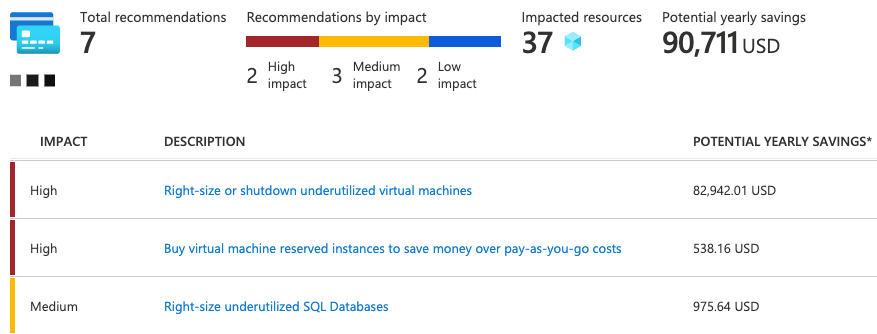
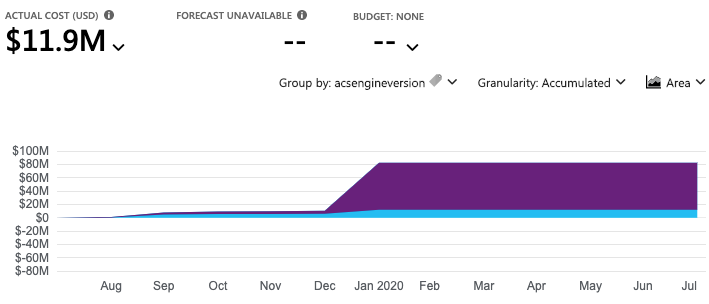
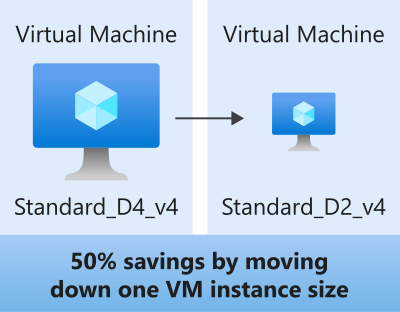

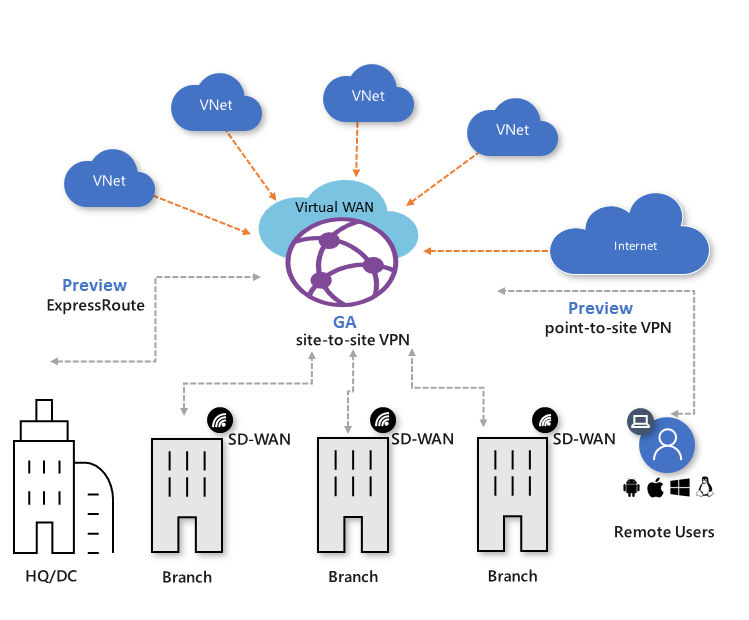
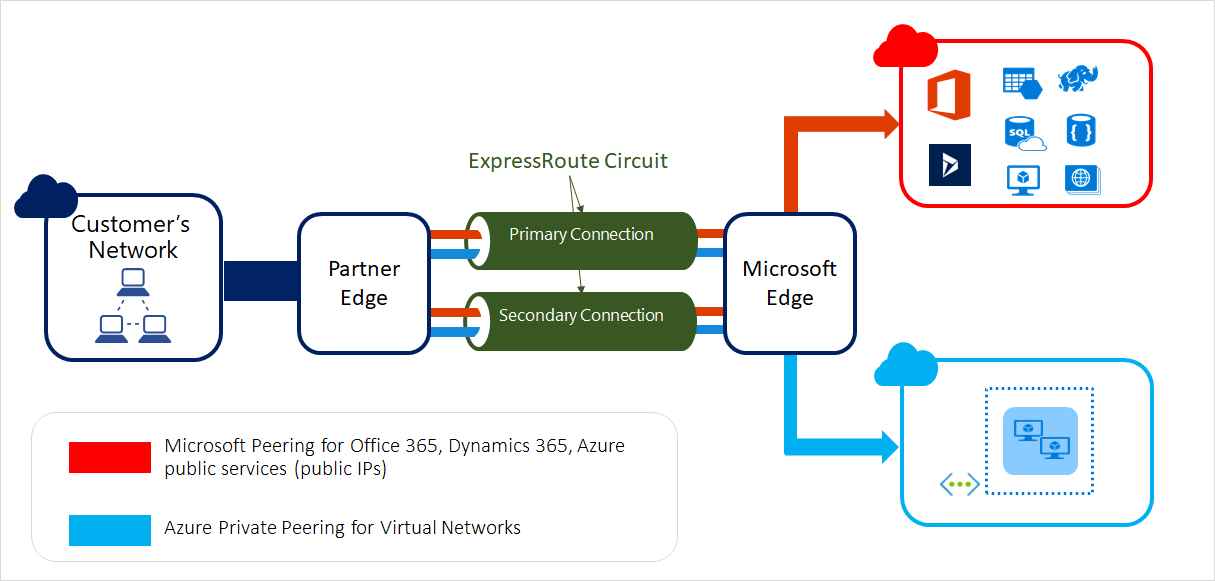
Azure Networking Services Illustration Slideshow
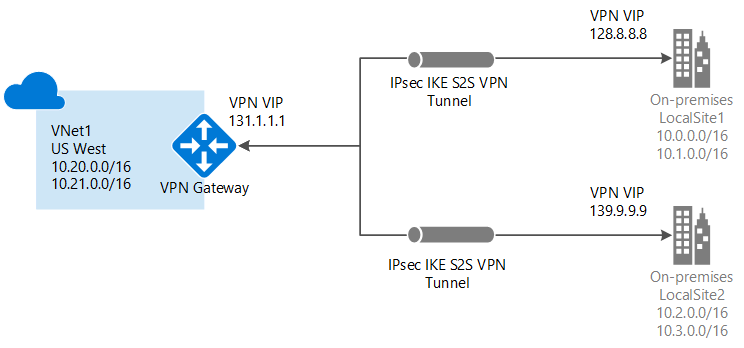

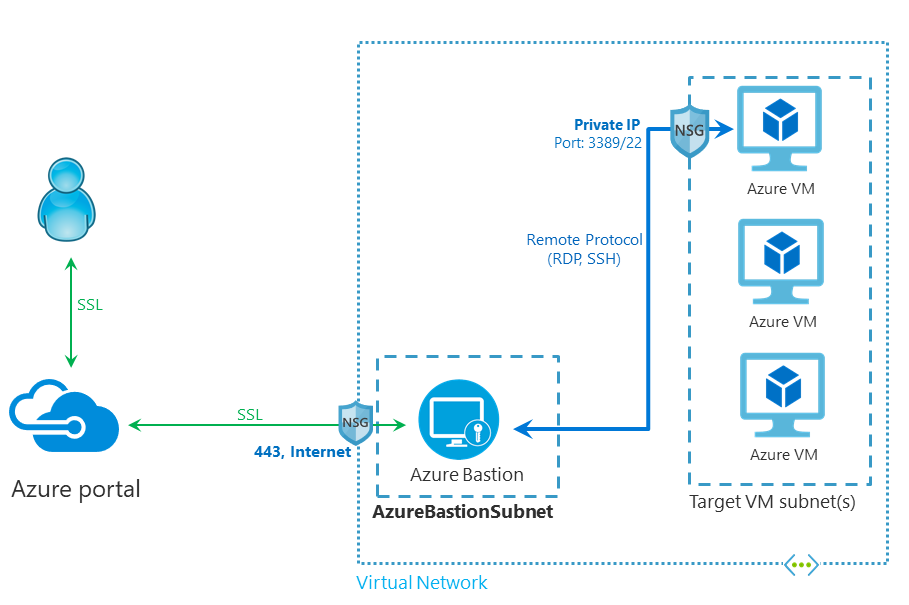
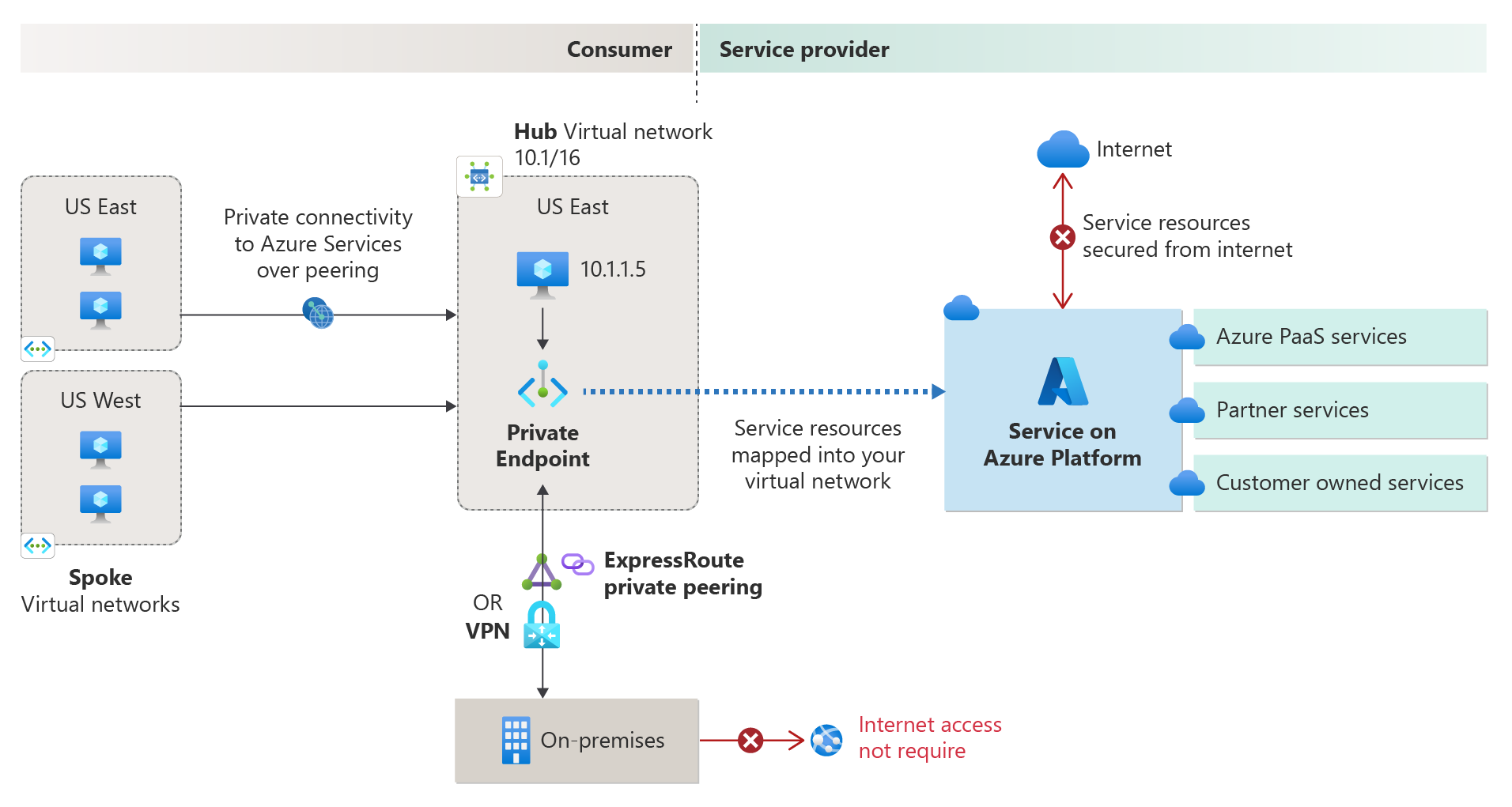
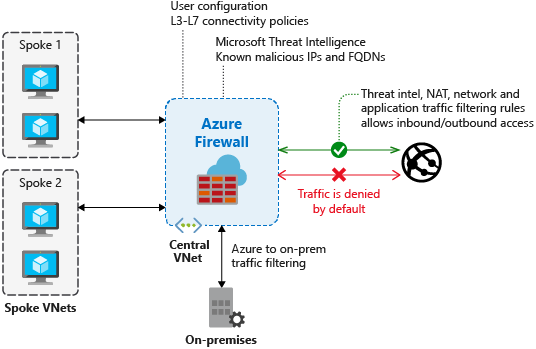
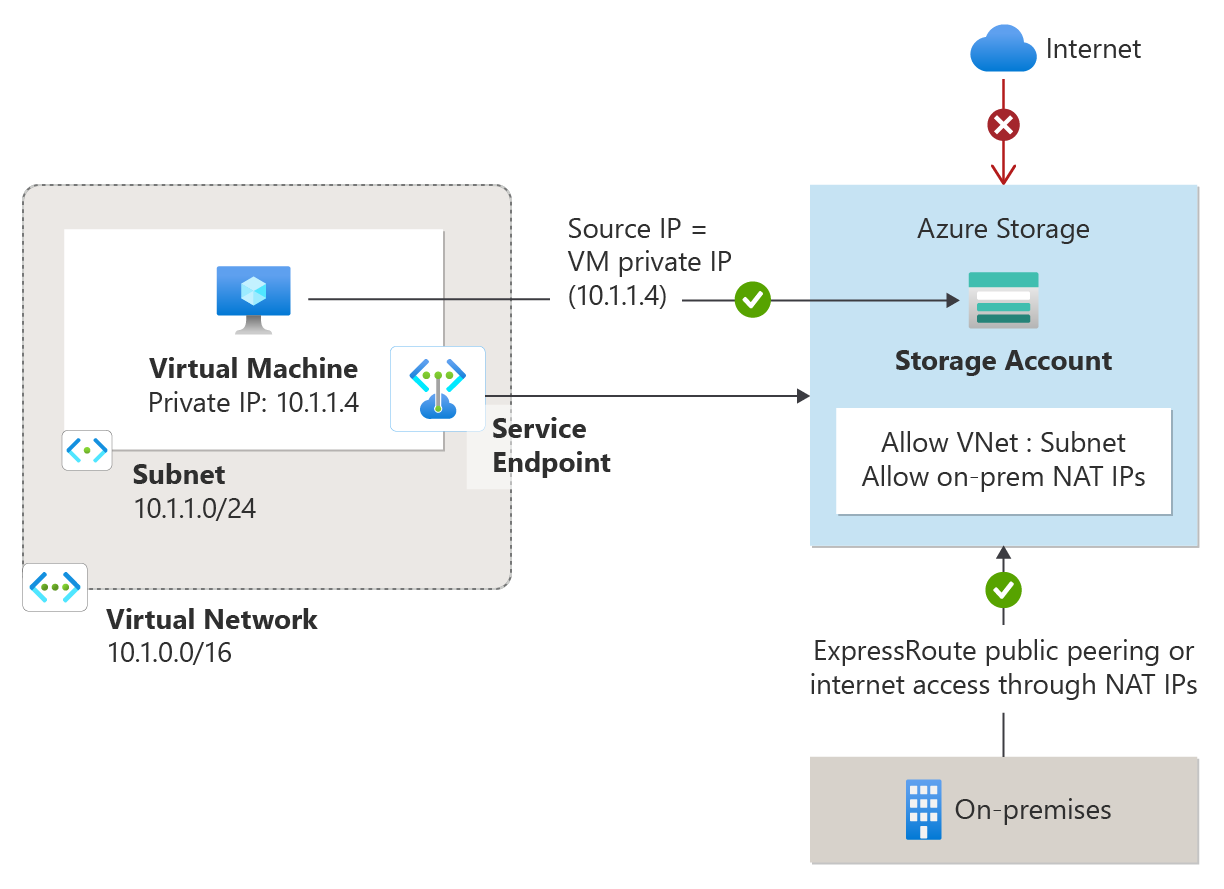
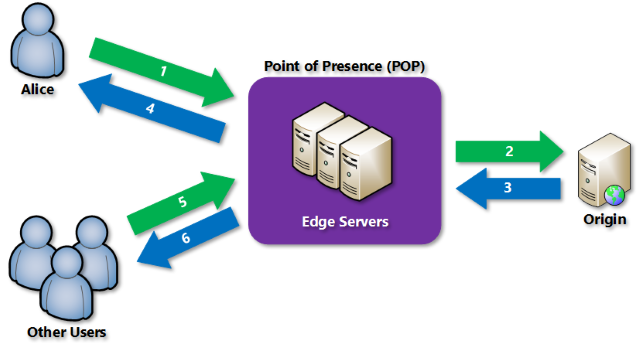
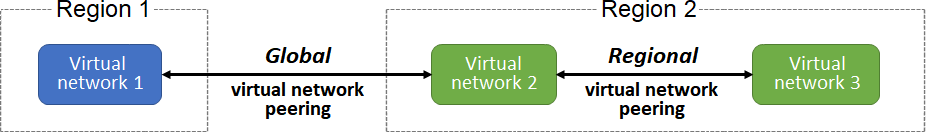

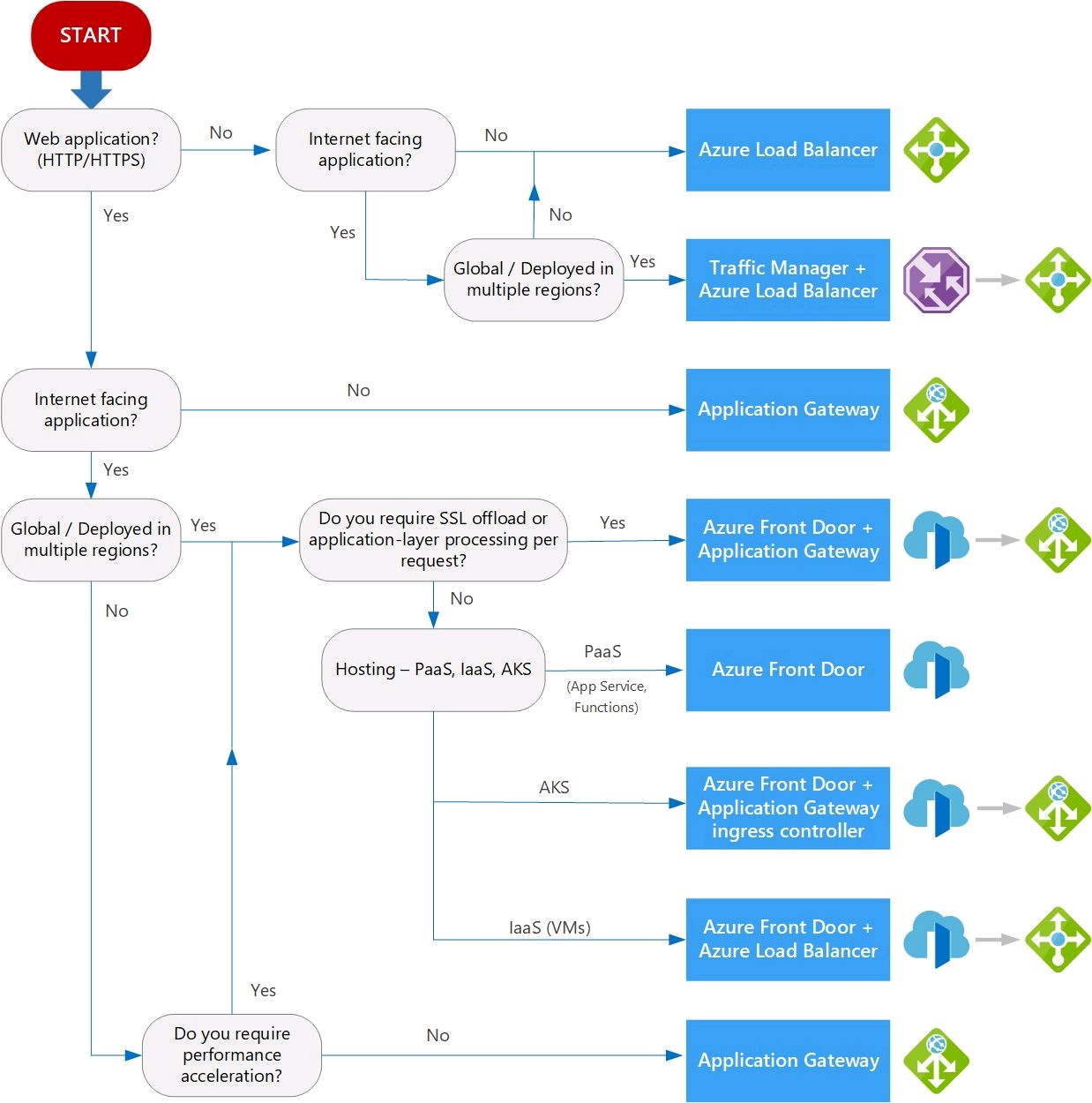
Azure AD Identity & Governance Slideshow
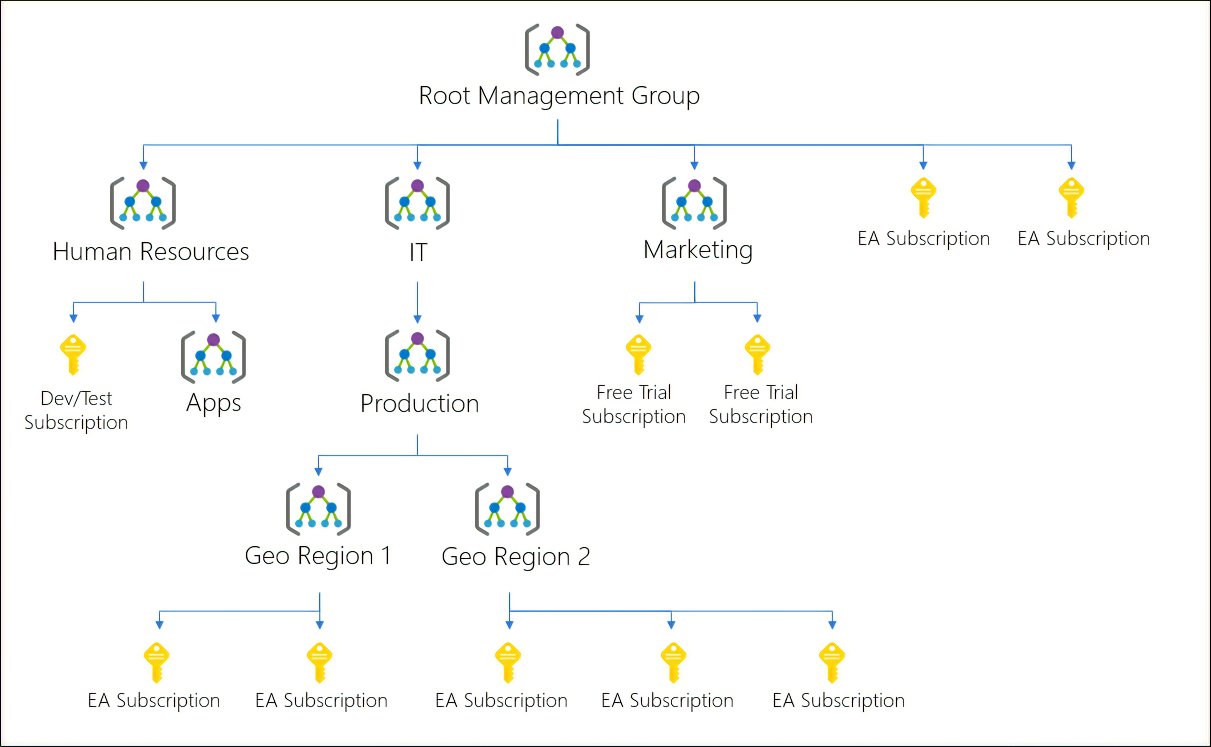
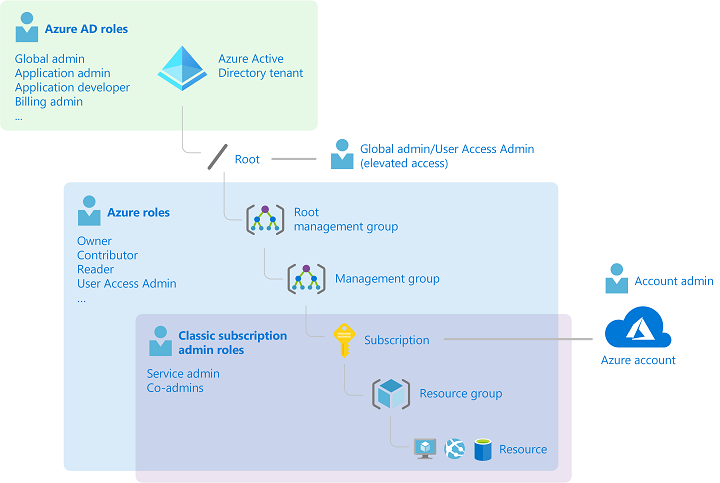
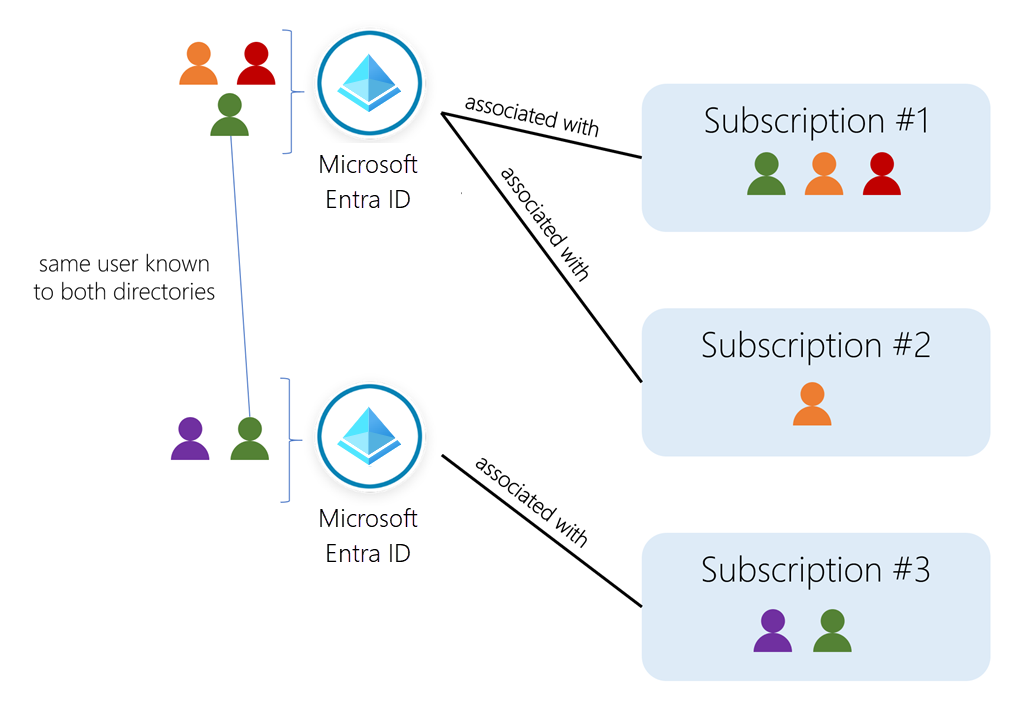
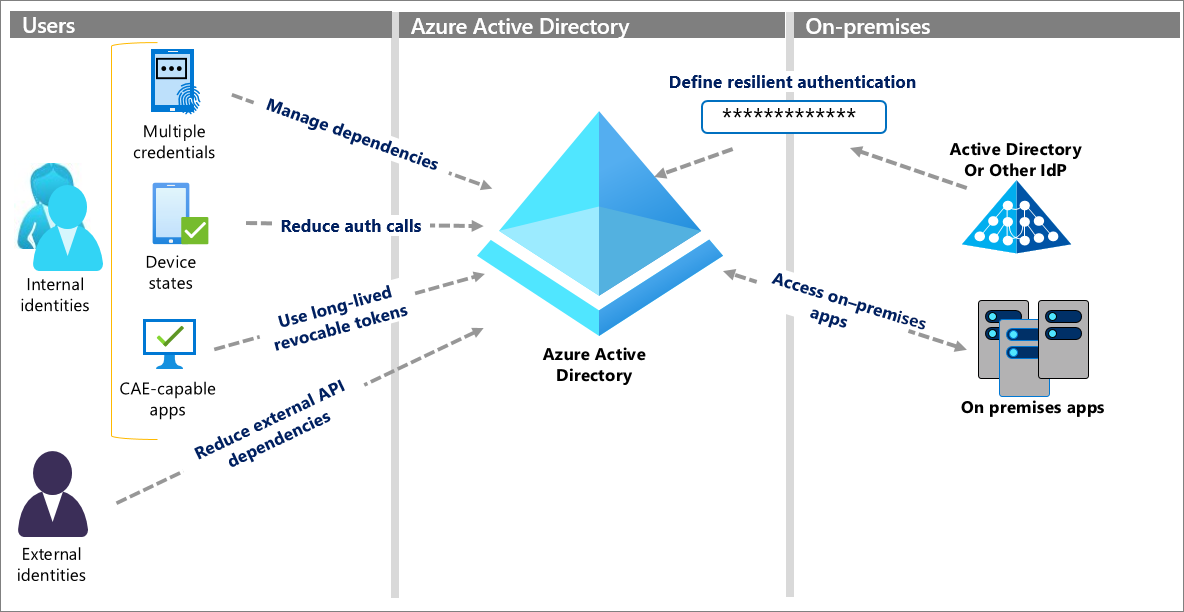
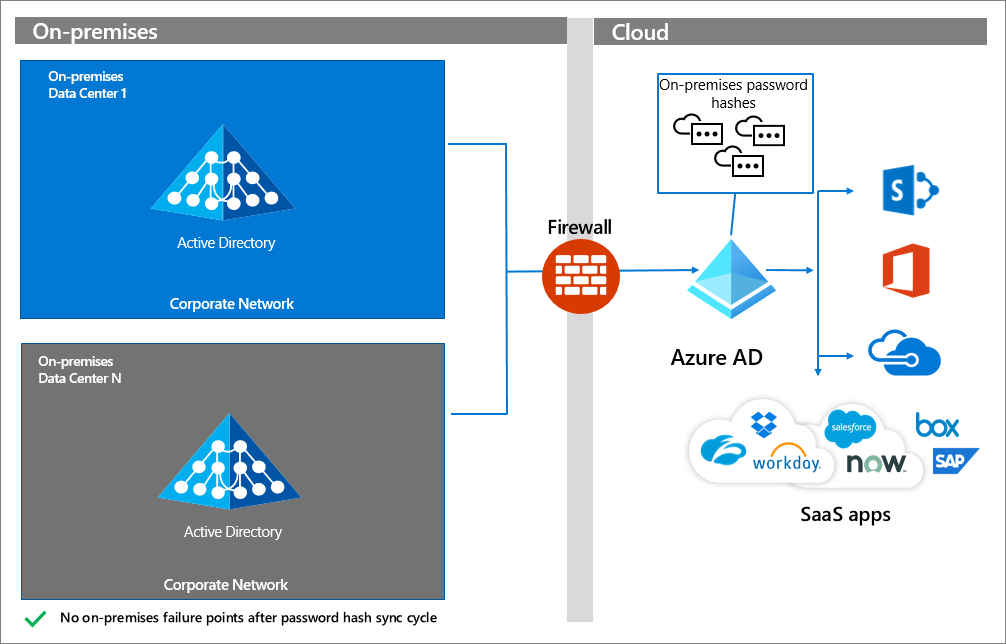
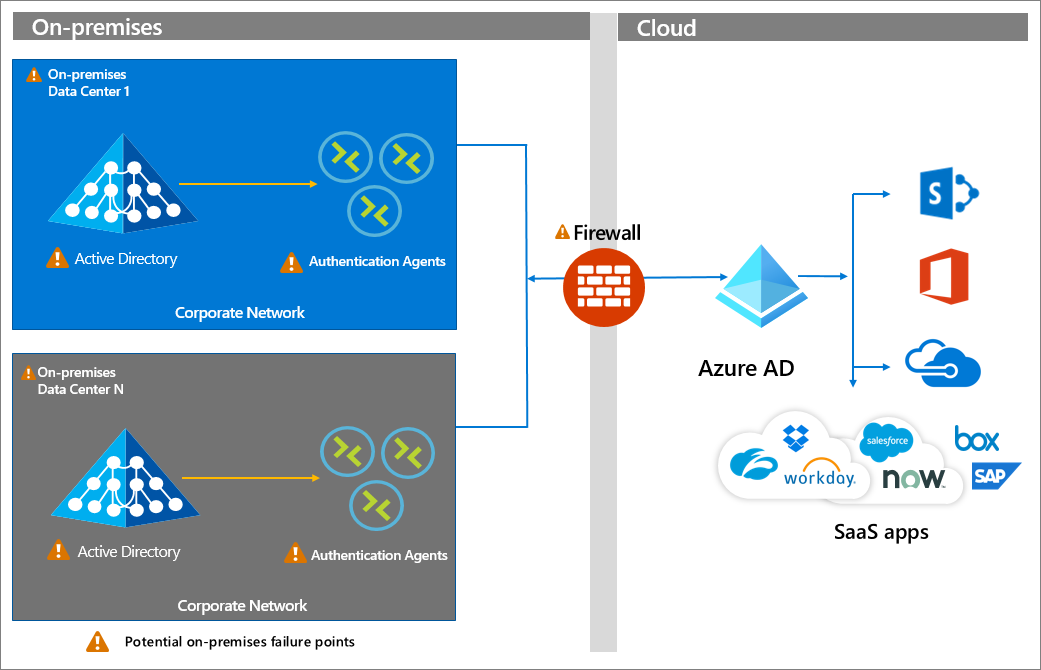
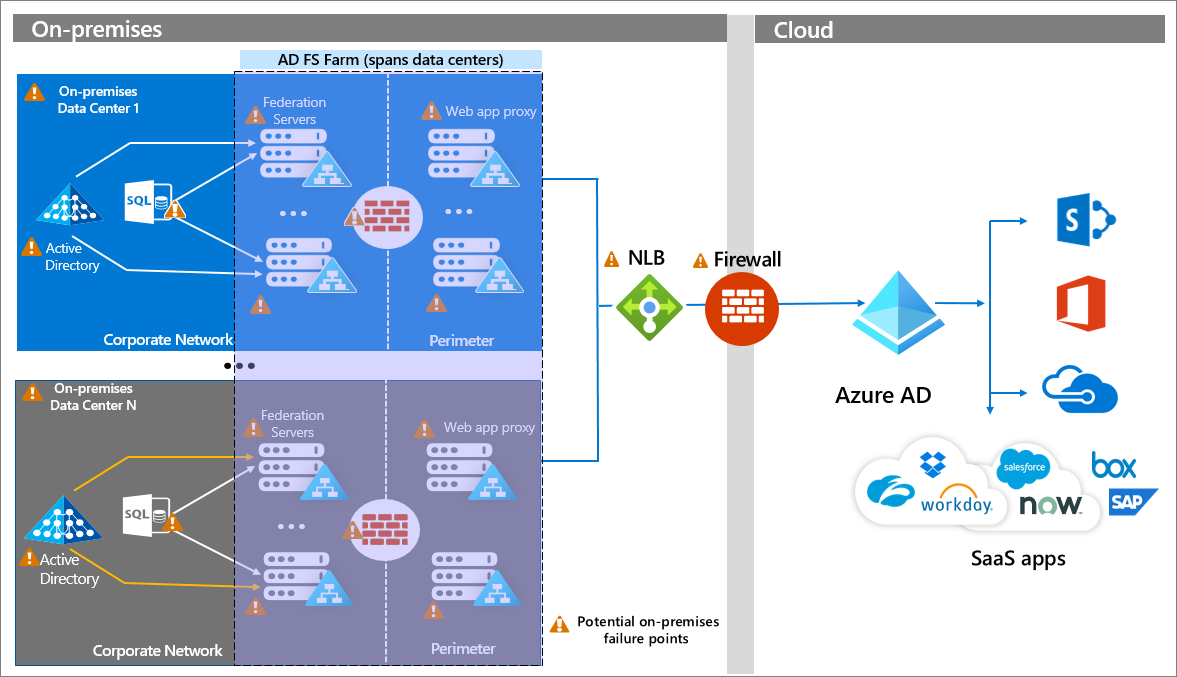
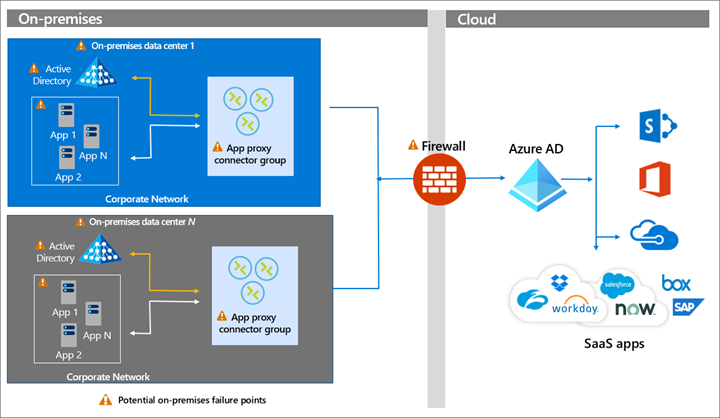
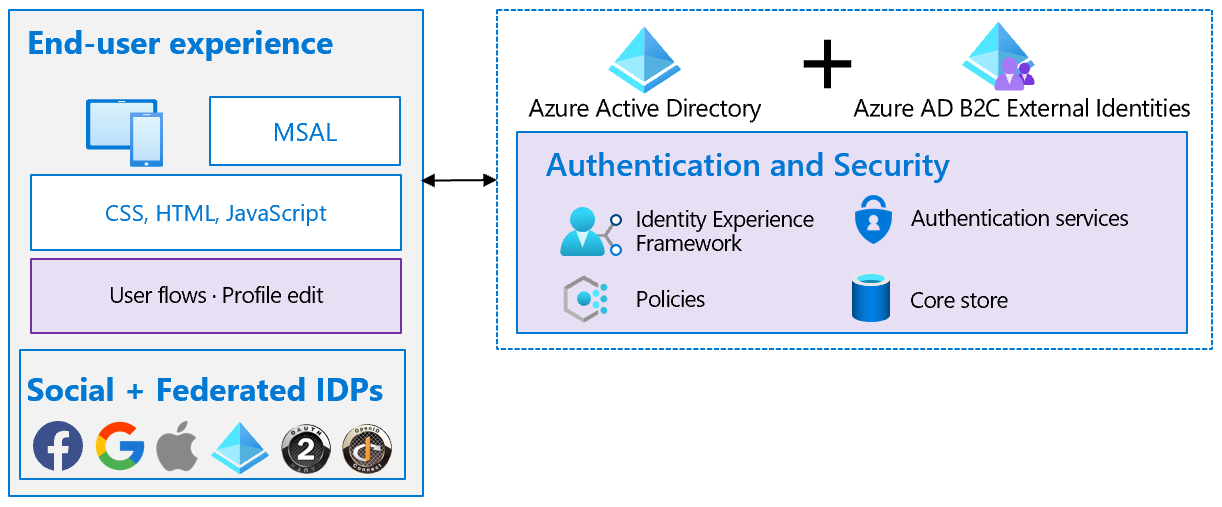
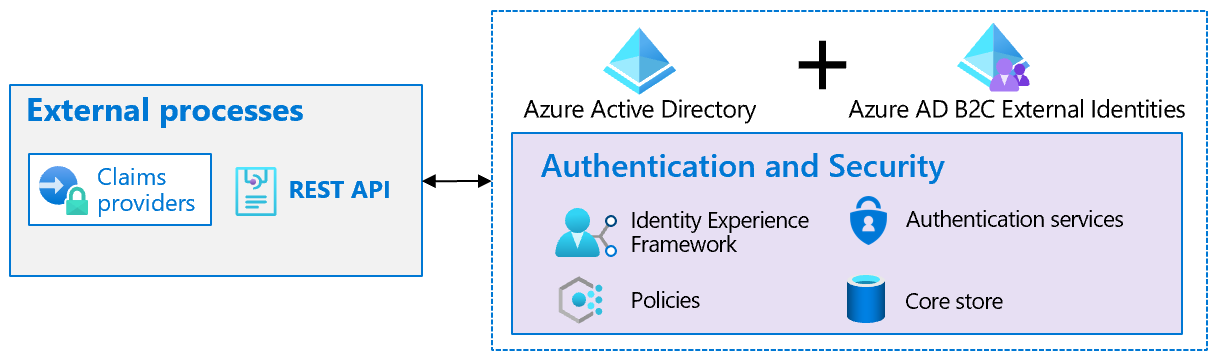
Deploy and Compute Azure Resources Slideshow
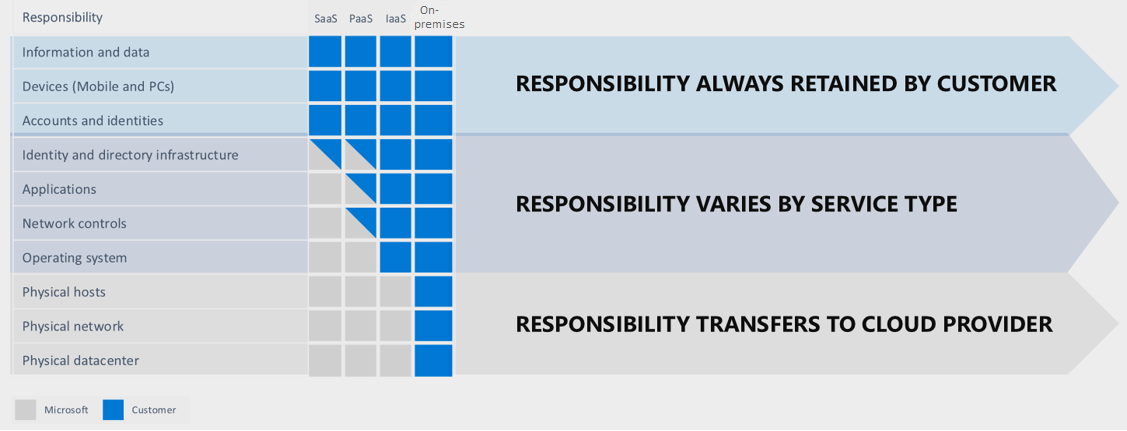
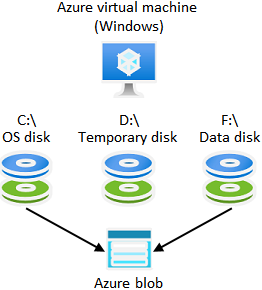






Monitor and Backup Azure Resources Slideshow


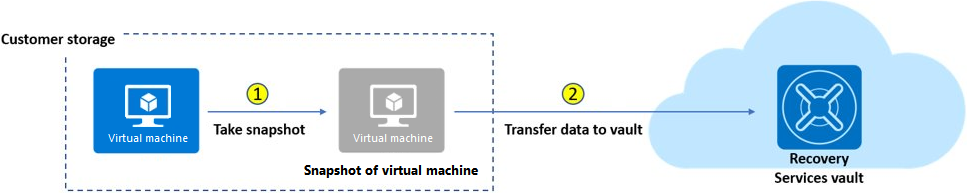

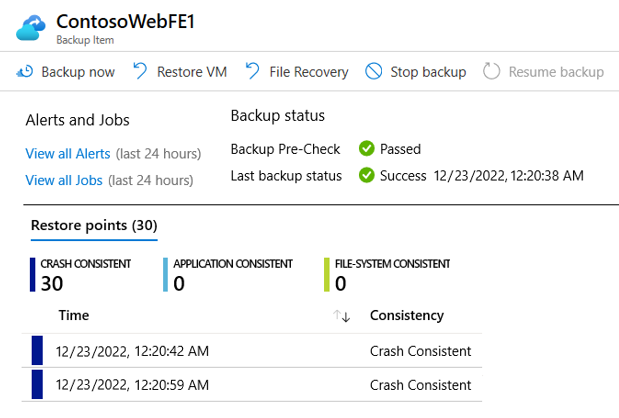


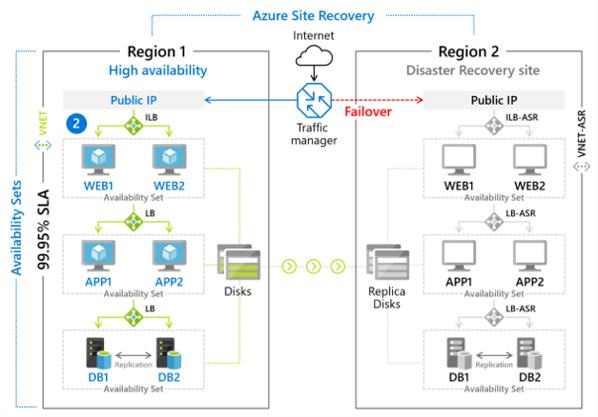
Implementation and Management of Azure Storage Slideshow