Question
Time left
Score
0
What is the answer to this questions?
A
Choice 1
B
Choice 2
C
Choice 3
D
Choice 4
Below are the skills measured in this category:
1
Describe Cloud Concepts (20-25%)
Identify the benefits and considerations of using cloud services:
identify the benefits of cloud computing, such as High Availability, Scalability, Elasticity,
Agility, and Disaster Recovery
identify the differences between Capital Expenditure (CapEx) and Operational
Expenditure (OpEx)
describe the consumption-based mode
2
Describe the differences between categories of cloud services
Describe the shared responsibility model
Describe Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS),
Describe Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
Describe Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
Describe Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Identify a service type based on a use case
3
Describe the differences between types of cloud computing
Define cloud computing
Describe Public cloud
Describe Private cloud
Describe Hybrid cloud
Describe Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Compare and contrast the three types of cloud computing
4
After completing the Cloud Concepts quizzes successfully, you should be able to:
Understand the benefits of cloud computing in Azure and how it can save you time and money
Explain cloud concepts such as high availability, scalability, elasticity, agility, and disaster recovery
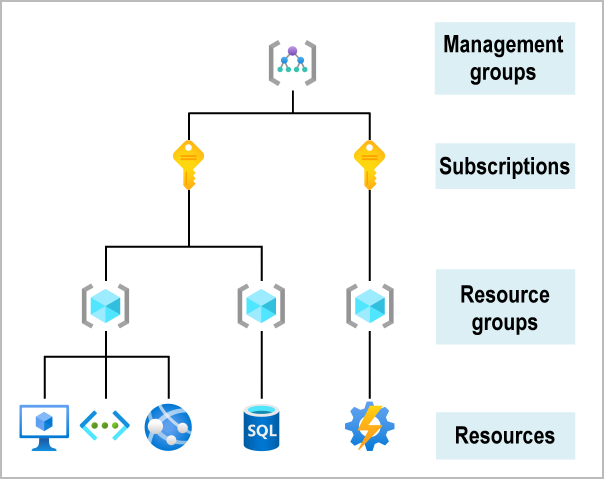
Describe core Azure architecture components such as subscriptions, management groups, resources and resource groups
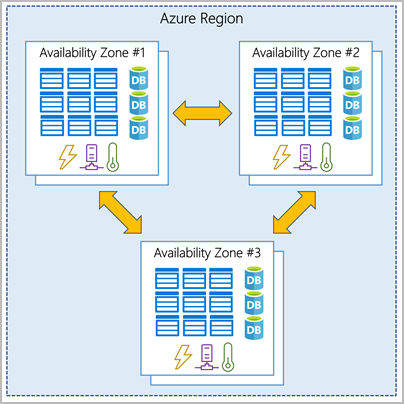
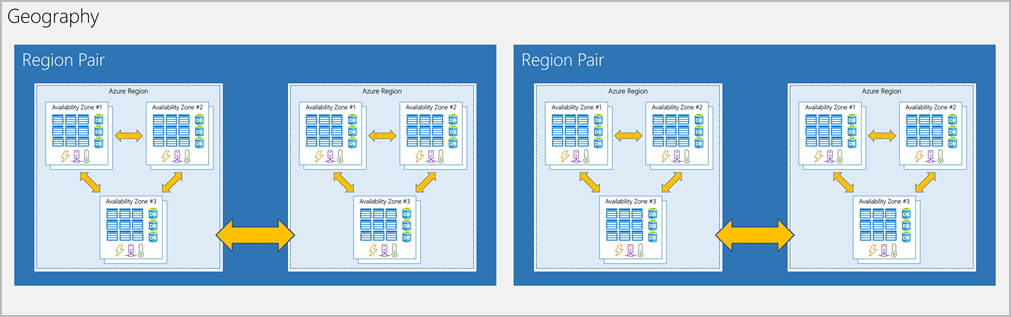
Summarize geographic distribution concepts such as Azure regions, region pairs, and availability zones
5
Describe core solutions and management tools on Azure (10-15%)
Describe core solutions available in Azure
Describe the benefits and usage of Internet of Things (IoT) Hub, IoT Central, and Azure
Sphere
Describe the benefits and usage of Azure Synapse Analytics, HDInsight, and Azure
Databricks
Describe the benefits and usage of Azure Machine Learning, Cognitive Services and
Azure Bot Service
Describe the benefits and usage of serverless computing solutions that include Azure
Functions and Logic Apps
Describe the benefits and usage of Azure DevOps, GitHub, GitHub Actions, and Azure
DevTest Labs
6
Describe Azure management tools
Describe the functionality and usage of the Azure Portal, Azure PowerShell, Azure CLI,
Cloud Shell, and Azure Mobile App
Describe the functionality and usage of Azure Advisor
Describe the functionality and usage of Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates
7
After completing this section, you should be able to:
Choose the correct Azure Artificial Intelligence service to address different kinds of business challenges.
Choose the best software development process tools and services for a given business scenario.
Choose the correct cloud monitoring service to address different kinds of business challenges.
Choose the correct Azure management tool to address different kinds of technical needs and challenges.
Choose the right serverless computing technology for your business scenario.
Choose the best Azure IoT service for a given business scenario.
After completing this section, you should be able to:
Choose the correct Azure Artificial Intelligence service to address different kinds of business challenges.
Choose the best software development process tools and services for a given business scenario.
Choose the correct cloud monitoring service to address different kinds of business challenges.
Choose the correct Azure management tool to address different kinds of technical needs and challenges.
Choose the right serverless computing technology for your business scenario.
Choose the best Azure IoT service for a given business scenario.
Below are some common Azure Cloud Concepts
0
What is cloud computing?
It's the delivery of computing services over the internet, which is otherwise known as the cloud. These services include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence. Cloud computing offers faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
1
What are some cloud computing advantages?
Reliability: Depending on the service-level agreement that you choose, your cloud-based applications can provide a continuous user experience with no apparent downtime even when things go wrong.
Scalability: Applications in the cloud can be scaled in two ways, while taking advantage of autoscaling:
- Vertically: Computing capacity can be increased by adding RAM or CPUs to a virtual machine.
- Horizontally: Computing capacity can be increased by adding instances of a resource, such as adding more virtual machines to your configuration.
Elasticity: Cloud-based applications can be configured to always have the resources they need.
Agility: Cloud-based resources can be deployed and configured quickly as your application requirements change.
Geo-distribution: Applications and data can be deployed to regional datacenters around the globe, so your customers always have the best performance in their region.
Disaster recovery: By taking advantage of cloud-based backup services, data replication, and geo-distribution, you can deploy your applications with the confidence that comes from knowing that your data is safe in the event that disaster should occur.
2
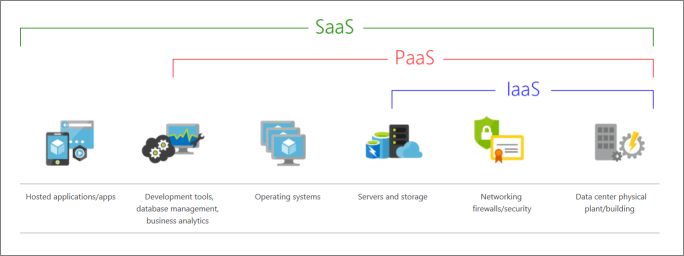
What are cloud service models?
IAAS:
This cloud service model is the closest to managing physical servers. A cloud provider keeps the hardware up to date, but operating system maintenance and network configuration is left to the cloud tenant. For example, Azure virtual machines are fully operational virtual compute devices running in Microsoft's datacenters. An advantage of this cloud service model is rapid deployment of new compute devices. Setting up a new virtual machine is considerably faster than procuring, installing, and configuring a physical server.
SAAS:
In this cloud service model, the cloud provider manages all aspects of the application environment, such as virtual machines, networking resources, data storage, and applications. The cloud tenant only needs to provide their data to the application managed by the cloud provider. For example, Office 365 provides a fully working version of Office that runs in the cloud. All that you need to do is create your content, and Office 365 takes care of everything else.
PAAS
This cloud service model is a managed hosting environment. The cloud provider manages the virtual machines and networking resources, and the cloud tenant deploys their applications into the managed hosting environment. For example, Azure App Services provides a managed hosting environment where developers can upload their web applications without having to deal with the physical hardware and software requirements.
DAAS
DAAS is a form of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), hosted in the cloud. With VDI, an organization deploys virtual desktops from its own on-premises data centers. In-house IT teams are responsible for deploying the virtual desktops as well as purchasing, managing, and upgrading the infrastructure.
3
What is serverless computing?
Overlapping with PaaS, serverless computing enables developers to build applications faster by eliminating the need for them to manage infrastructure. With serverless applications, the cloud service provider automatically provisions, scales, and manages the infrastructure required to run the code. Serverless architectures are highly scalable and event-driven. They use resources only when a specific function or trigger occurs.
4
What are public, private, and hybrid clouds?
Public cloud Services are offered over the public internet and available to anyone who wants to purchase them. Cloud resources like servers and storage are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider and delivered over the internet.
Private cloud Computing resources are used exclusively by users from one business or organization. A private cloud can be physically located at your organization's on-site datacenter. It also can be hosted by a third-party service provider.
Hybrid cloud This computing environment combines a public cloud and a private cloud by allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
5
What can I do with Azure?
Azure provides more than 100 services that enable you to do everything from running your existing applications on virtual machines to exploring new software paradigms, such as intelligent bots and mixed reality.
Many teams start exploring the cloud by moving their existing applications to virtual machines that run in Azure. Migrating your existing apps to virtual machines is a good start, but the cloud is much more than a different place to run your virtual machines.
For example, Azure provides AI and machine-learning services that can naturally communicate with your users through vision, hearing, and speech. It also provides storage solutions that dynamically grow to accommodate massive amounts of data. Azure services enable solutions that aren't feasible without the power of the cloud.
6
Which of the following choices isn't a cloud computing category: NAAS, PAAS, SAAS, IAAS, DAAS?
- Networking-as-a-Service (NaaS)
- NaaS isn't a cloud computing category.
7
Which of the following statements is true about Operating Expenses (OpEx)?
-With Operating Expenses (OpEx), you are only responsible for the computing resources that you use.
8
Is Distributed cloud a type of cloud computing?
- A distributed cloud isn't a valid type of cloud computing.
9
Is Geographic isolation a benefit of using cloud services?
- You can choose to create resources in a single region; however, one of the primary advantages to cloud computing is geographic distribution.
10
What can be used to manage governance across multiple Azure subscriptions?
- Management groups facilitate the hierarchical ordering of Azure resources into collections, at a level of scope above subscriptions. Distinct governance conditions can be applied to each management group, with Azure Policy and Azure role-based access controls, to manage Azure subscriptions effectively. The resources and subscriptions assigned to a management group automatically inherit the conditions applied to the management group.
11
What is a logical unit of Azure services that links to an Azure account?
- An Azure subscription is a logical unit of Azure services that links to an Azure account.
12
Can Resource Groups be nested?
- Azure resource groups can't be nested