Recent Score:
Take the Test again Go Home
Resources
0
What is Azure?
Azure is a cloud computing platform with an ever-expanding set of services to help you build solutions to meet your business goals. Azure services range from simple web services for hosting your business presence in the cloud to running fully virtualized computers for you to run your custom software solutions. Azure provides a wealth of cloud-based services like remote storage, database hosting, and centralized account management. Azure also offers new capabilities like AI and Internet of Things (IoT).
1
What is Azure VM temporary storage?
In Azure, every VM – regardless if Linux or Windows – gets a temporary disk assigned automatically. This temporary disk is located on the physical server (the hypervisor) where the Azure VM is hosted and is non-persistent. Disks used by the operating system or additionally added data disks are persistent disks and stored in Azure Storage.
Azure VM’s can be moved from its current host to new host at any time due to maintenance, hardware failures or other reasons. In such an event, the data from the temporary storage will not preserve or moved to the new host. Apart from the hardware failures, there are many other reasons data from the temporary disk will be lost:
Resizing of the VM
Restarting of the VM
Moving from one host to another
Updating/upgrading of host
2
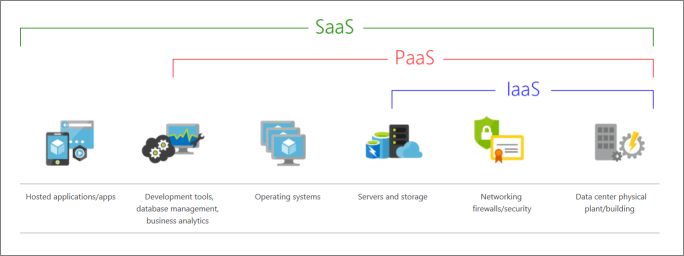
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) lets you provision individual VMs along with the associated networking and storage components. Then you deploy whatever software and applications you want onto those VMs. This model is the closest to a traditional on-premises environment, except that Microsoft manages the infrastructure. You still manage the individual VMs.
3
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) provides a managed hosting environment, where you can deploy your application without needing to manage VMs or networking resources. Azure App Service is a PaaS service.
4
Functions-as-a-Service (FaaS)
Functions-as-a-Service (FaaS) goes even further in removing the need to worry about the hosting environment. In a FaaS model, you simply deploy your code and the service automatically runs it. Azure Functions are a FaaS service.
5
Software as a service (SaaS)
Software as a service (SaaS) allows users to connect to and use cloud-based apps over the internet. Common examples are email, calendar, and office tools, such as Microsoft Office 365.
6
Serverless computing
Serverless computing is the abstraction of servers, infrastructure, and operating systems. When you build serverless apps, you don’t need to provision and manage any servers, so you don't have to worry about infrastructure. Serverless computing is driven by the reaction to events and triggers happening in near-real time in the cloud.
7
Economies of scale
Cloud providers such as Microsoft, Google, and Amazon are large businesses that leverage the benefits of economies of scale and then pass the savings on to their customers.
8
Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) offers developers a global solution for rapidly delivering high-bandwidth content to users by caching their content at strategically placed physical nodes around the world. Azure CDN can also accelerate dynamic content, which cannot be cached, by leveraging various network optimizations using CDN POPs.
9
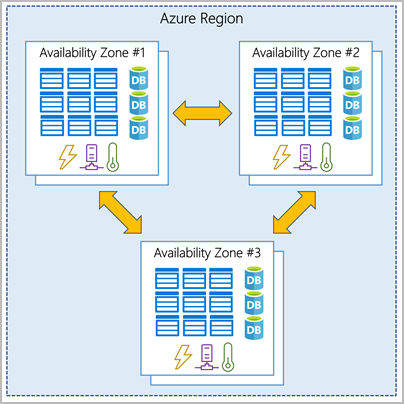
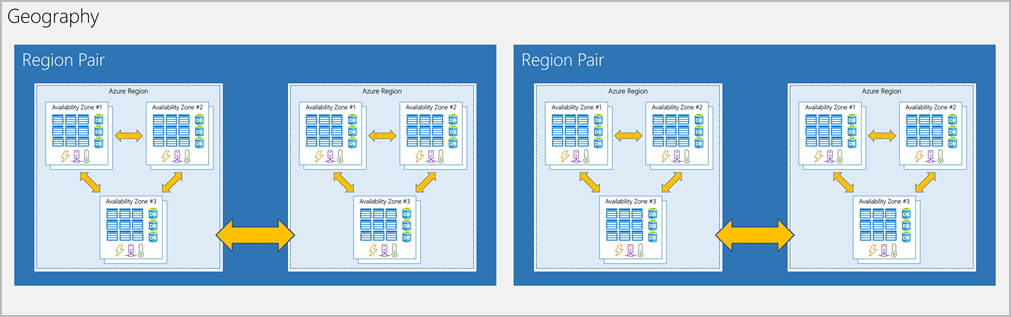
Fault tolerance
Fault tolerance is the property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of one or more of its components. In Azure, it refers to ensuring that a portion of the production systems are available online (via a failover cluster, available set, or available zone) if a subset of the system components (or an entire data center) goes offline.
10
CAPex
Server costs are considered CapEx and include all server hardware components and the cost of supporting them. When purchasing servers, make sure to design for fault tolerance and redundancy (e.g., server clustering, redundant power supplies, and uninterruptible power supplies). When a server needs to be replaced or added to a data center, you need to pay for the computer. This can affect your immediate cash flow because you must pay for the server up front.